The domain within your query sequence starts at position 79 and ends at position 194; the E-value for the REC domain shown below is 2e-48.
LLVFTKEDSQCNGFHRACEKAGFKCTVTKEVQTVLTCFQDKLHDIIIIDHRYPRQMDAET LCRSIRSSKFSENTVIVGVVRRVDKEESSLMPFLAAGFTRRFIENPNVMACYNELL
The domain was found using the schnipsel database
RECcheY-homologous receiver domain |
|---|
| SMART accession number: | SM00448 |
|---|---|
| Description: | CheY regulates the clockwise rotation of E. coli flagellar motors. This domain contains a phosphoacceptor site that is phosphorylated by histidine kinase homologues. |
| Interpro abstract (IPR001789): | Two-component signal transduction systems enable bacteria to sense, respond, and adapt to a wide range of environments, stressors, and growth conditions [ (PUBMED:16176121) ]. Some bacteria can contain up to as many as 200 two-component systems that need tight regulation to prevent unwanted cross-talk [ (PUBMED:18076326) ]. These pathways have been adapted to response to a wide variety of stimuli, including nutrients, cellular redox state, changes in osmolarity, quorum signals, antibiotics, and more [ (PUBMED:12372152) ]. Two-component systems are comprised of a sensor histidine kinase (HK) and its cognate response regulator (RR) [ (PUBMED:10966457) ]. The HK catalyses its own auto-phosphorylation followed by the transfer of the phosphoryl group to the receiver domain on RR; phosphorylation of the RR usually activates an attached output domain, which can then effect changes in cellular physiology, often by regulating gene expression. Some HK are bifunctional, catalysing both the phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of their cognate RR. The input stimuli can regulate either the kinase or phosphatase activity of the bifunctional HK. A variant of the two-component system is the phospho-relay system. Here a hybrid HK auto-phosphorylates and then transfers the phosphoryl group to an internal receiver domain, rather than to a separate RR protein. The phosphoryl group is then shuttled to histidine phosphotransferase (HPT) and subsequently to a terminal RR, which can evoke the desired response [ (PUBMED:11934609) (PUBMED:11489844) ]. Bipartite response regulator proteins are involved in a two-component signal transduction system in bacteria, and certain eukaryotes like protozoa, that functions to detect and respond to environmental changes [ (PUBMED:7699720) ]. These systems have been detected during host invasion, drug resistance, motility, phosphate uptake, osmoregulation, and nitrogen fixation, amongst others [ (PUBMED:12015152) ]. The two-component system consists of a histidine protein kinase environmental sensor that phosphorylates the receiver domain of a response regulator protein; phosphorylation induces a conformational change in the response regulator, which activates the effector domain, triggering the cellular response [ (PUBMED:10966457) ]. The domains of the two-component proteins are highly modular, but the core structures and activities are maintained. The response regulators act as phosphorylation-activated switches to affect a cellular response, usually by transcriptional regulation. Most of these proteins consist of two domains, an N-terminal response regulator receiver domain, and a variable C-terminal effector domain with DNA-binding activity. This entry represents the response regulator receiver domain, which belongs to the CheY family, and receives the signal from the sensor partner in the two-component system. |
| GO process: | phosphorelay signal transduction system (GO:0000160) |
| Family alignment: |
There are 909786 REC domains in 870260 proteins in SMART's nrdb database.
Click on the following links for more information.
- Evolution (species in which this domain is found)
-
Taxonomic distribution of proteins containing REC domain.
This tree includes only several representative species. The complete taxonomic breakdown of all proteins with REC domain is also avaliable.
Click on the protein counts, or double click on taxonomic names to display all proteins containing REC domain in the selected taxonomic class.
- Cellular role (predicted cellular role)
-
Cellular role: signalling
- Literature (relevant references for this domain)
-
Primary literature is listed below; Automatically-derived, secondary literature is also avaliable.
- Pao GM, SaierMHJ r
- Response regulators of bacterial signal transduction systems: selective domain shuffling during evolution.
- J Mol Evol. 1995; 40: 136-54
- Display abstract
Response regulators of bacterial sensory transduction systems generally consist of receiver module domains covalently linked to effector domains. The effector domains include DNA binding and/or catalytic units that are regulated by sensor kinase-catalyzed aspartyl phosphorylation within their receiver modules. Most receiver modules are associated with three distinct families of DNA binding domains, but some are associated with other types of DNA binding domains, with methylated chemotaxis protein (MCP) demethylases, or with sensor kinases. A few exist as independent entities which regulate their target systems by noncovalent interactions. In this study the molecular phylogenies of the receiver modules and effector domains of 49 fully sequenced response regulators and their homologues were determined. The three major, evolutionarily distinct, DNA binding domains found in response regulators were evaluated for their phylogenetic relatedness, and the phylogenetic trees obtained for these domains were compared with those for the receiver modules. Members of one family (family 1) of DNA binding domains are linked to large ATPase domains which usually function cooperatively in the activation of E. coli sigma 54-dependent promoters or their equivalents in other bacteria. Members of a second family (family 2) always function in conjunction with the E. coli sigma 70 or its equivalent in other bacteria. A third family of DNA binding domains (family 3) functions by an uncharacterized mechanism involving more than one sigma factor. These three domain families utilize distinct helix-turn-helix motifs for DNA binding. The phylogenetic tree of the receiver modules revealed three major and several minor clusters of these domains. The three major receiver module clusters (clusters 1, 2, and 3) generally function with the three major families of DNA binding domains (families 1, 2, and 3, respectively) to comprise three classes of response regulators (classes 1, 2, and 3), although several exceptions exist. The minor clusters of receiver modules were usually, but not always, associated with other types of effector domains. Finally, several receiver modules did not fit into a cluster. It was concluded that receiver modules usually diverged from common ancestral protein domains together with the corresponding effector domains, although domain shuffling, due to intragenic splicing and fusion, must have occurred during the evolution of some of these proteins. Multiple sequence alignments of the 49 receiver modules and their various types of effector domains, together with other homologous domains, allowed definition of regions of striking sequence similarity and degrees of conservation of specific residues. Sequence data were correlated with structure/function when such information was available.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
- Volz K
- Structural conservation in the CheY superfamily.
- Biochemistry. 1993; 32: 11741-53
- Stock JB, Stock AM, Mottonen JM
- Signal transduction in bacteria.
- Nature. 1990; 344: 395-400
- Display abstract
Cells display a remarkable ability to respond to small fluctuations in their surroundings. In simple microbial systems, information from sensory receptors feeds into a circuitry of regulatory proteins that transfer high energy phosphoryl groups from histidine to aspartate side chains. This phosphotransfer network couples environmental signals to an array of response elements that control cell motility and regulate gene expression.
- Stock AM, Mottonen JM, Stock JB, Schutt CE
- Three-dimensional structure of CheY, the response regulator of bacterial chemotaxis.
- Nature. 1989; 337: 745-9
- Display abstract
Homologies among bacterial signal transduction proteins suggest that a common mechanism mediates processes such as chemotaxis, osmoregulation, sporulation, virulence, and responses to nitrogen, phosphorous and oxygen deprivation. A common kinase-mediated phosphotransfer reaction has recently been identified in chemotaxis, nitrogen regulation, and osmoregulation. In chemotaxis, the CheA kinase passes a phosphoryl group to the cytoplasmic protein CheY, which functions as a phosphorylation-activated switch that interacts with flagellar components to regulate motility. We report here the X-ray crystal structure of the Salmonella typhimurium CheY protein. The determination of the structure was facilitated by the use of site-specific mutagenesis to engineer heavy-atom binding sites. CheY is a single-domain protein composed of a doubly wound five-stranded parallel beta-sheet. The phosphoacceptor site in CheY is probably a cluster of aspartic-acid side chains near the C-terminal edge of the beta-sheet. The pattern of sequence similarity of CheY with components of other regulatory systems can be interpreted in the light of the CheY structure and supports the view that this family of proteins have a common structural motif and active site.
- Drlica K, Rouviere-Yaniv J
- Histonelike proteins of bacteria.
- Microbiol Rev. 1987; 51: 301-19
- Metabolism (metabolic pathways involving proteins which contain this domain)
-
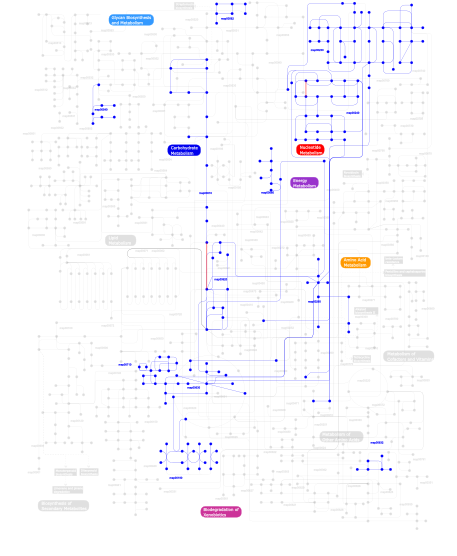
Click the image to view the interactive version of the map in iPath% proteins involved KEGG pathway ID Description 77.92 map02020 Two-component system - General 16.71 map02030 Bacterial chemotaxis - General 4.51 map03090 Type II secretion system 0.24  map00240
map00240Pyrimidine metabolism 0.14  map00230
map00230Purine metabolism 0.05  map00620
map00620Pyruvate metabolism 0.05 map04910 Insulin signaling pathway 0.05  map00010
map00010Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis 0.05  map00710
map00710Carbon fixation 0.05 map04930 Type II diabetes mellitus 0.05  map00540
map00540Lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis 0.02  map00260
map00260Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism 0.02  map00680
map00680Methane metabolism 0.02  map00562
map00562Inositol phosphate metabolism 0.02  map00190
map00190Oxidative phosphorylation 0.02  map00630
map00630Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism 0.02 map02010 ABC transporters - General 0.02  map00632
map00632Benzoate degradation via CoA ligation 0.02 map00633 Trinitrotoluene degradation This information is based on mapping of SMART genomic protein database to KEGG orthologous groups. Percentage points are related to the number of proteins with REC domain which could be assigned to a KEGG orthologous group, and not all proteins containing REC domain. Please note that proteins can be included in multiple pathways, ie. the numbers above will not always add up to 100%.
- Structure (3D structures containing this domain)
3D Structures of REC domains in PDB
PDB code Main view Title 1a04 
THE STRUCTURE OF THE NITRATE/NITRITE RESPONSE REGULATOR PROTEIN NARL IN THE MONOCLINIC C2 CRYSTAL FORM 1a0o 
CHEY-BINDING DOMAIN OF CHEA IN COMPLEX WITH CHEY 1a2o 
STRUCTURAL BASIS FOR METHYLESTERASE CHEB REGULATION BY A PHOSPHORYLATION-ACTIVATED DOMAIN 1ab5 
STRUCTURE OF CHEY MUTANT F14N, V21T 1ab6 
STRUCTURE OF CHEY MUTANT F14N, V86T 1b00 
PHOB RECEIVER DOMAIN FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI 1bdj 
COMPLEX STRUCTURE OF HPT DOMAIN AND CHEY 1c4w 
1.9 A STRUCTURE OF A-THIOPHOSPHONATE MODIFIED CHEY D57C 1cey 
ASSIGNMENTS, SECONDARY STRUCTURE, GLOBAL FOLD, AND DYNAMICS OF CHEMOTAXIS Y PROTEIN USING THREE-AND FOUR-DIMENSIONAL HETERONUCLEAR (13C,15N) NMR SPECTROSCOPY 1chn 
MAGNESIUM BINDING TO THE BACTERIAL CHEMOTAXIS PROTEIN CHEY RESULTS IN LARGE CONFORMATIONAL CHANGES INVOLVING ITS FUNCTIONAL SURFACE 1cye 
THREE DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF CHEMOTACTIC CHE Y PROTEIN IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION BY NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE METHODS 1d4z 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CHEY-95IV, A HYPERACTIVE CHEY MUTANT 1d5w 
PHOSPHORYLATED FIXJ RECEIVER DOMAIN 1dbw 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF FIXJ-N 1dc7 
STRUCTURE OF A TRANSIENTLY PHOSPHORYLATED ""SWITCH"" IN BACTERIAL SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION 1dc8 
STRUCTURE OF A TRANSIENTLY PHOSPHORYLATED ""SWITCH"" IN BACTERIAL SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION 1dcf 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE RECEIVER DOMAIN OF THE ETHYLENE RECEPTOR OF ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA 1dck 
STRUCTURE OF UNPHOSPHORYLATED FIXJ-N COMPLEXED WITH MN2+ 1dcm 
STRUCTURE OF UNPHOSPHORYLATED FIXJ-N WITH AN ATYPICAL CONFORMER (MONOMER A) 1djm 
SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF BEF3-ACTIVATED CHEY FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI 1dz3 
DOMAIN-SWAPPING IN THE SPORULATION RESPONSE REGULATOR SPO0A 1e6k 
Two-component signal transduction system D12A mutant of CheY 1e6l 
Two-component signal transduction system D13A mutant of CheY 1e6m 
D57A mutant of CheY 1eay 
CHEY-BINDING (P2) DOMAIN OF CHEA IN COMPLEX WITH CHEY FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI 1ehc 
STRUCTURE OF SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PROTEIN CHEY 1f4v 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF ACTIVATED CHEY BOUND TO THE N-TERMINUS OF FLIM 1f51 
A TRANSIENT INTERACTION BETWEEN TWO PHOSPHORELAY PROTEINS TRAPPED IN A CRYSTAL LATTICE REVEALS THE MECHANISM OF MOLECULAR RECOGNITION AND PHOSPHOTRANSFER IN SINGAL TRANSDUCTION 1ffg 
CHEY-BINDING DOMAIN OF CHEA IN COMPLEX WITH CHEY AT 2.1 A RESOLUTION 1ffs 
CHEY-BINDING DOMAIN OF CHEA IN COMPLEX WITH CHEY FROM CRYSTALS SOAKED IN ACETYL PHOSPHATE 1ffw 
CHEY-BINDING DOMAIN OF CHEA IN COMPLEX WITH CHEY WITH A BOUND IMIDO DIPHOSPHATE 1fqw 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF ACTIVATED CHEY 1fsp 
NMR SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS SPO0F PROTEIN, 20 STRUCTURES 1hey 
INVESTIGATING THE STRUCTURAL DETERMINANTS OF THE P21-LIKE TRIPHOSPHATE AND MG2+ BINDING SITE 1i3c 
RESPONSE REGULATOR FOR CYANOBACTERIAL PHYTOCHROME, RCP1 1j56 
MINIMIZED AVERAGE STRUCTURE OF BERYLLOFLUORIDE-ACTIVATED NTRC RECEIVER DOMAIN: MODEL STRUCTURE INCORPORATING ACTIVE SITE CONTACTS 1jbe 
1.08 A Structure of apo-Chey reveals meta-active conformation 1jlk 
Crystal structure of the Mn(2+)-bound form of response regulator Rcp1 1k66 
Crystal Structure of the Cyanobacterial Phytochrome Response Regulator, RcpB 1k68 
Crystal Structure of the Phosphorylated Cyanobacterial Phytochrome Response Regulator RcpA 1kgs 
Crystal Structure at 1.50 A of an OmpR/PhoB Homolog from Thermotoga maritima 1kmi 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF AN E.COLI CHEMOTAXIS PROTEIN, CHEZ 1krw 
SOLUTION STRUCTURE AND BACKBONE DYNAMICS OF BERYLLOFLUORIDE-ACTIVATED NTRC RECEIVER DOMAIN 1krx 
SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF BERYLLOFLUORIDE-ACTIVATED NTRC RECEIVER DOMAIN: MODEL STRUCTURES INCORPORATING ACTIVE SITE CONTACTS 1l5y 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF MG2+ / BEF3-BOUND RECEIVER DOMAIN OF SINORHIZOBIUM MELILOTI DCTD 1l5z 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE E121K SUBSTITUTION OF THE RECEIVER DOMAIN OF SINORHIZOBIUM MELILOTI DCTD 1m5t 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE RESPONSE REGULATOR DIVK 1m5u 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE RESPONSE REGULATOR DIVK. STRUCTURE AT PH 8.0 IN THE APO-FORM 1mav 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE RESPONSE REGULATOR DIVK AT PH 6.0 IN COMPLEX WITH MN2+ 1mb0 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE RESPONSE REGULATOR DIVK AT PH 8.0 IN COMPLEX WITH MN2+ 1mb3 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE RESPONSE REGULATOR DIVK AT PH 8.5 IN COMPLEX WITH MG2+ 1mih 
A ROLE FOR CHEY GLU 89 IN CHEZ-MEDIATED DEPHOSPHORYLATION OF THE E. COLI CHEMOTAXIS RESPONSE REGULATOR CHEY 1mvo 
Crystal structure of the PhoP receiver domain from Bacillus subtilis 1nat 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF SPOOF FROM BACILLUS SUBTILIS 1ntr 
SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE N-TERMINAL RECEIVER DOMAIN OF NTRC 1nxo 
MicArec pH7.0 1nxp 
MicArec pH4.5 1nxs 
MicArec pH4.9 1nxt 
MicArec pH 4.0 1nxv 
MicArec pH 4.2 1nxw 
MicArec pH 5.1 1nxx 
MicArec pH 5.5 1ny5 
Crystal structure of sigm54 activator (AAA+ ATPase) in the inactive state 1oxb 
Complex between YPD1 and SLN1 response regulator domain in space group P2(1)2(1)2(1) 1oxk 
Complex between YPD1 and SLN1 response regulator domain in space group P3(2) 1p2f 
Crystal Structure Analysis of Response Regulator DrrB, a Thermotoga maritima OmpR/PhoB Homolog 1p6q 
NMR Structure of the Response regulator CheY2 from Sinorhizobium meliloti, complexed with Mg++ 1p6u 
NMR structure of the BeF3-activated structure of the response regulator Chey2-Mg2+ from Sinorhizobium meliloti 1pey 
Crystal structure of the Response Regulator Spo0F complexed with Mn2+ 1pux 
NMR Solution Structure of BeF3-Activated Spo0F, 20 conformers 1qkk 
Crystal structure of the receiver domain and linker region of DctD from Sinorhizobium meliloti 1qmp 
Phosphorylated aspartate in the crystal structure of the sporulation response regulator, Spo0A 1rnl 
THE NITRATE/NITRITE RESPONSE REGULATOR PROTEIN NARL FROM NARL 1s8n 
Crystal structure of Rv1626 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis 1sd5 
Crystal structure of Rv1626 1srr 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A PHOSPHATASE RESISTANT MUTANT OF SPORULATION RESPONSE REGULATOR SPO0F FROM BACILLUS SUBTILIS 1tmy 
CHEY FROM THERMOTOGA MARITIMA (APO-I) 1u0s 
Chemotaxis kinase CheA P2 domain in complex with response regulator CheY from the thermophile thermotoga maritima 1u8t 
Crystal structure of CheY D13K Y106W alone and in complex with a FliM peptide 1udr 
CHEY MUTANT WITH LYS 91 REPLACED BY ASP, LYS 92 REPLACED BY ALA, ILE 96 REPLACED BY LYS AND ALA 98 REPLACED BY LEU (STABILIZING MUTATIONS IN HELIX 4) 1vlz 
UNCOUPLED PHOSPHORYLATION AND ACTIVATION IN BACTERIAL CHEMOTAXIS: THE 2.1 ANGSTROM STRUCTURE OF A THREONINE TO ISOLEUCINE MUTANT AT POSITION 87 OF CHEY 1w25 
Response regulator PleD in complex with c-diGMP 1xhe 
Crystal structure of the receiver domain of redox response regulator arca 1xhf 
Crystal structure of the bef3-activated receiver domain of redox response regulator arca 1yio 
Crystallographic structure of response regulator StyR from Pseudomonas fluorescens 1ymu 
SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PROTEIN CHEY MUTANT WITH MET 17 REPLACED BY GLY (M17G) 1ymv 
SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PROTEIN CHEY MUTANT WITH PHE 14 REPLACED BY GLY, SER 15 REPLACED BY GLY, AND MET 17 REPLACED BY GLY 1ys6 
Crystal structure of the response regulatory protein PrrA from Mycobacterium Tuberculosis 1ys7 
Crystal structure of the response regulator protein prrA comlexed with Mg2+ 1zdm 
Crystal Structure of Activated CheY Bound to Xe 1zes 
BeF3- activated PhoB receiver domain 1zgz 
Crystal Structure Of The Receiver Domain Of TMAO Respiratory System Response Regulator TorR 1zh2 
Crystal Structure Of The Calcium-Bound Receiver Domain Of Kdp Potassium Transport System Response Regulator KdpE 1zh4 
Crystal Structure Of The Mg+2/BeF3-Bound Receiver Domain Of Kdp Potassium Transport System Response Regulator KdpE 1zit 
Structure of the receiver domain of NtrC4 from Aquifex aeolicus 1zn2 
Low Resolution Structure of Response Regulator StyR 1zy2 
Crystal structure of the phosphorylated receiver domain of the transcription regulator NtrC1 from Aquifex aeolicus 2a9o 
Crystal structures of an activated YycF homologue, the essential response regulator from S.pneumoniae in complex with BeF3 and the effect of pH on BeF3 binding, possible phosphate in the active site 2a9p 
Medium Resolution BeF3 bound RR02-rec 2a9q 
Low Resolution Structure RR02-rec on BeF3 bound 2a9r 
RR02-Rec Phosphate in the active site 2ayx 
Solution structure of the E.coli RcsC C-terminus (residues 700-949) containing linker region and phosphoreceiver domain 2ayz 
Solution structure of the E.coli RcsC C-terminus (residues 817-949) containing phosphoreceiver domain 2b1j 
Crystal Structure of Unphosphorylated CheY Bound to the N-Terminus of FliM 2b4a 
Crystal structure of a response regulator receiver domain protein (bh3024) from bacillus halodurans c-125 at 2.42 A resolution 2che 
STRUCTURE OF THE MG2+-BOUND FORM OF CHEY AND MECHANISM OF PHOSPHORYL TRANSFER IN BACTERIAL CHEMOTAXIS 2chf 
STRUCTURE OF THE MG2+-BOUND FORM OF CHEY AND THE MECHANISM OF PHOSPHORYL TRANSFER IN BACTERIAL CHEMOTAXIS 2chy 
THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF CHEY, THE RESPONSE REGULATOR OF BACTERIAL CHEMOTAXIS 2fka 
Crystal structure of Mg(2+) and BeF(3)(-)-bound CheY in complex with CheZ(200-214) solved from a F432 crystal grown in CAPS (pH 10.5) 2flk 
Crystal structure of CheY in complex with CheZ(200-214) solved from a F432 crystal grown in CAPS (pH 10.5) 2flw 
Crystal structure of Mg2+ and BeF3- ound CheY in complex with CheZ 200-214 solved from a F432 crystal grown in Hepes (pH 7.5) 2fmf 
Crystal structure of CheY in complex with CheZ 200-214 solved from a F432 crystal grown in Hepes (pH 7.5) 2fmh 
Crystal structure of Mg2+ and BeF3- bound CheY in complex with CheZ 200-214 solved from a F432 crystal grown in Tris (pH 8.4) 2fmi 
Crystal structure of CheY in complex with CheZ 200-214 solved from a F432 crystal grown in Tris (pH 8.4) 2fmk 
Crystal structure of Mg2+ and BeF3- bound CheY in complex with CheZ 200-214 solved from a P2(1)2(1)2 crystal grown in MES (pH 6.0) 2fsp 
NMR SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS SPO0F PROTEIN, MINIMIZED AVERAGE STRUCTURE 2ftk 
berylloflouride Spo0F complex with Spo0B 2gkg 
Receiver domain from Myxococcus xanthus social motility protein FrzS 2gwr 
Crystal structure of the response regulator protein mtrA from Mycobacterium Tuberculosis 2hqo 
Structure of a Atypical Orphan Response Regulator Protein Revealed a New Phosphorylation-Independent Regulatory Mechanism 2hqr 
Structure of a Atypical Orphan Response Regulator Protein Revealed a New Phosphorylation-Independent Regulatory Mechanism 2i6f 
Receiver domain from Myxococcus xanthus social motility protein FrzS 2id7 
1.75 A Structure of T87I Phosphono-CheY 2id9 
1.85 A Structure of T87I/Y106W Phosphono-CheY 2idm 
2.00 A Structure of T87I/Y106W Phosphono-CheY 2iyn 
The co-factor-induced pre-active conformation in PhoB 2j48 
NMR structure of the pseudo-receiver domain of the CikA protein. 2jb9 
PhoB response regulator receiver domain constitutively-active double mutant D10A and D53E. 2jba 
PhoB response regulator receiver domain constitutively-active double mutant D53A and Y102C. 2jk1 
Crystal structure of the wild-type HupR receiver domain 2jrl 
Solution structure of the beryllofluoride-activated NtrC4 receiver domain dimer 2jvi 
NMR Solution Structure of the Hyper-Sporulation Response Regulator Spo0F Mutant H101A from Bacillus subtilis 2jvj 
NMR Solution Structure of the Hyper-Sporulation Response Regulator Spo0F Mutant I90A from Bacillus subtilis 2jvk 
NMR Solution Structure of the Hyper-Sporulation Response Regulator Spo0F Mutant L66A from Bacillus subtilis 2lle 
Computational design of an eight-stranded (beta/alpha)-barrel from fragments of different folds 2lp4 
Solution structure of P1-CheY/P2 complex in bacterial chemotaxis 2lpm 
Chemical Shift and Structure Assignments for Sma0114 2m98 
NMR Structure of BeF3 Activated Sma0114 2msk 
2MSK 2msl 
2MSL 2msw 
2MSW 2n9u 
2N9U 2nt3 
Receiver domain from Myxococcus xanthus social motility protein FrzS (Y102A Mutant) 2nt4 
Receiver domain from Myxococcus xanthus social motility protein FrzS (H92F mutant) 2oqr 
The structure of the response regulator RegX3 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis 2pkx 
E.coli response regulator PhoP receiver domain 2pl1 
Berrylium Fluoride activated receiver domain of E.coli PhoP 2pl9 
Crystal Structure of CheY-Mg(2+)-BeF(3)(-) in Complex with CheZ(C19) Peptide solved from a P2(1)2(1)2 Crystal 2pln 
Crystal structure analysis of HP1043, an orphan resonse regulator of h. pylori 2pmc 
Crystal Structure of CheY-Mg(2+) in Complex with CheZ(C15) Peptide solved from a P1 Crystal 2qr3 
Crystal structure of the N-terminal signal receiver domain of two-component system response regulator from Bacteroides fragilis 2qsj 
Crystal structure of a LuxR family DNA-binding response regulator from Silicibacter pomeroyi 2qv0 
Crystal structure of the response regulatory domain of protein mrkE from Klebsiella pneumoniae 2qvg 
The crystal structure of a two-component response regulator from Legionella pneumophila 2qxy 
Crystal structure of a response regulator from Thermotoga maritima 2qzj 
Crystal structure of a two-component response regulator from Clostridium difficile 2r25 
Complex of YPD1 and SLN1-R1 with bound Mg2+ and BeF3- 2rdm 
Crystal structure of response regulator receiver protein from Sinorhizobium medicae WSM419 2rjn 
Crystal structure of an uncharacterized protein Q2BKU2 from Neptuniibacter caesariensis 2tmy 
CHEY FROM THERMOTOGA MARITIMA (APO-II) 2v0n 
ACTIVATED RESPONSE REGULATOR PLED IN COMPLEX WITH C-DIGMP AND GTP- ALPHA-S 2vuh 
Crystal structure of the D55E mutant of the HupR receiver domain 2vui 
Crystal structure of the HupR receiver domain in inhibitory phospho- state 2wb4 
activated diguanylate cyclase PleD in complex with c-di-GMP 2zay 
Crystal structure of response regulator from Desulfuromonas acetoxidans 2zwm 
Crystal structure of YycF receiver domain from Bacillus subtilis 3a0r 
Crystal structure of histidine kinase ThkA (TM1359) in complex with response regulator protein TrrA (TM1360) 3a0u 
Crystal structure of response regulator protein TrrA (TM1360) from Thermotoga maritima in complex with Mg(2+)-BeF (wild type) 3a10 
Crystal structure of response regulator protein TrrA (TM1360) from Thermotoga maritima in complex with Mg(2+)-BeF (SeMet, L89M) 3b2n 
Crystal structure of DNA-binding response regulator, LuxR family, from Staphylococcus aureus 3bre 
Crystal Structure of P.aeruginosa PA3702 3c3m 
Crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of response regulator receiver protein from Methanoculleus marisnigri JR1 3c3w 
Crystal Structure of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Hypoxic Response Regulator DosR 3c97 
Crystal structure of the response regulator receiver domain of a signal transduction histidine kinase from Aspergillus oryzae 3cfy 
Crystal structure of signal receiver domain of putative Luxo repressor protein from Vibrio parahaemolyticus 3cg0 
Crystal structure of signal receiver domain of modulated diguanylate cyclase from Desulfovibrio desulfuricans G20, an example of alternate folding 3cg4 
Crystal structure of response regulator receiver domain protein (CheY-like) from Methanospirillum hungatei JF-1 3chy 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI CHEY REFINED AT 1.7-ANGSTROM RESOLUTION 3cnb 
Crystal structure of signal receiver domain of DNA binding response regulator protein (merR) from Colwellia psychrerythraea 34H 3crn 
Crystal structure of response regulator receiver domain protein (CheY-like) from Methanospirillum hungatei JF-1 3cu5 
Crystal structure of a two component transcriptional regulator AraC from Clostridium phytofermentans ISDg 3cwo 
A beta/alpha-barrel built by the combination of fragments from different folds 3cz5 
Crystal structure of two-component response regulator, LuxR family, from Aurantimonas sp. SI85-9A1 3dge 
Structure of a histidine kinase-response regulator complex reveals insights into Two-component signaling and a novel cis-autophosphorylation mechanism 3dgf 
Structure of a histidine kinase-response regulator complex reveals insights into Two-component signaling and a novel cis-autophosphorylation mechanism 3dzd 
Crystal structure of sigma54 activator NTRC4 in the inactive state 3eod 
Crystal structure of N-terminal domain of E. coli RssB 3eq2 
Structure of Hexagonal Crystal form of Pseudomonas aeruginosa RssB 3eqz 
Crystal structure of a response regulator from Colwellia psychrerythraea 3eul 
Structure of the signal receiver domain of the putative response regulator NarL from Mycobacterium tuberculosis 3f6c 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF N-TERMINAL DOMAIN OF POSITIVE TRANSCRIPTION REGULATOR evgA FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI 3f6p 
Crystal Structure of unphosphorelated receiver domain of YycF 3f7a 
Structure of Orthorhombic crystal form of Pseudomonas aeruginosa RssB 3f7n 
Crystal Structure of CheY triple mutant F14E, N59M, E89L complexed with BeF3- and Mn2+ 3fft 
Crystal Structure of CheY double mutant F14E, E89R complexed with BeF3- and Mn2+ 3ffw 
Crystal Structure of CheY triple mutant F14Q, N59K, E89Y complexed with BeF3- and Mn2+ 3ffx 
Crystal Structure of CheY triple mutant F14E, N59R, E89H complexed with BeF3- and Mn2+ 3fgz 
Crystal Structure of CheY triple mutant F14E, N59M, E89R complexed with BeF3- and Mn2+ 3gl9 
The structure of a histidine kinase-response regulator complex sheds light into two-component signaling and reveals a novel cis autophosphorylation mechanism 3grc 
Crystal structure of a sensor protein from Polaromonas sp. JS666 3gt7 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF SIGNAL RECEIVER DOMAIN OF SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION HISTIDINE KINASE FROM Syntrophus aciditrophicus 3gwg 
Crystal structure of CheY of Helicobacter pylori 3h1e 
Crystal structure of Mg(2+) and BeH(3)(-)-bound CheY of Helicobacter pylori 3h1f 
Crystal structure of CheY mutant D53A of Helicobacter pylori 3h1g 
Crystal structure of Chey mutant T84A of helicobacter pylori 3h5i 
Crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of a response regulator/sensory box/GGDEF 3-domain protein from Carboxydothermus hydrogenoformans 3hdg 
Crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of an uncharacterized protein (WS1339) from Wolinella succinogenes 3hdv 
Crystal structure of response regulator receiver protein from Pseudomonas putida 3heb 
Crystal Structure of Response regulator receiver domain from Rhodospirillum rubrum 3hv2 
Crystal structure of signal receiver domain OF HD domain-containing protein FROM Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5 3hzh 
Crystal structure of the CheX-CheY-BeF3-Mg+2 complex from Borrelia burgdorferi 3i42 
Structure of response regulator receiver domain (CheY-like) from Methylobacillus flagellatus 3i5a 
Crystal structure of full-length WpsR from Pseudomonas syringae 3ilh 
Crystal structure of Two component response regulator from Cytophaga hutchinsonii 3jte 
Crystal structure of response regulator receiver domain Protein from clostridium thermocellum 3kcn 
The crystal structure of adenylate cyclase from Rhodopirellula baltica 3kht 
Crystal structure of response regulator from Hahella chejuensis 3kto 
Crystal structure of response regulator receiver protein from Pseudoalteromonas atlantica 3kyi 
Crystal structure of the phosphorylated P1 domain of CheA3 in complex with CheY6 from R. sphaeroides 3kyj 
Crystal structure of the P1 domain of CheA3 in complex with CheY6 from R. sphaeroides 3lte 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF RESPONSE REGULATOR (SIGNAL RECEIVER DOMAIN) FROM Bermanella marisrubri 3lua 
Crystal structure of a Signal receiver domain of Two component Signal Transduction (Histidine Kinase) from Clostridium thermocellum 3luf 
Structure of probable two-component system response regulator/GGDEF domain protein 3m6m 
Crystal structure of RpfF complexed with REC domain of RpfC 3mf4 
Crystal structure of putative two-component system response regulator/ggdef domain protein 3mm4 
Crystal structure of the receiver domain of the histidine kinase CKI1 from Arabidopsis thaliana 3mmn 
Crystal structure of the receiver domain of the histidine kinase CKI1 from Arabidopsis thaliana complexed with Mg2+ 3myy 
Structure of E. Coli CheY mutant A113P bound to Beryllium fluoride 3n0r 
Structure of the PhyR stress response regulator at 1.25 Angstrom resolution 3n53 
Crystal structure of a response regulator receiver modulated diguanylate cyclase from Pelobacter carbinolicus 3nhm 
Crystal structure of a response regulator from Myxococcus xanthus 3nhz 
Structure of N-terminal Domain of MtrA 3nnn 
BeF3 Activated DrrD Receiver Domain 3nns 
BeF3 Activated DrrB Receiver Domain 3olv 
Structural and functional effects of substitution at position T+1 in CheY: CheYA88V-BeF3-Mg complex 3olw 
Structural and functional effects of substitution at position T+1 in CheY: CheYA88T-BeF3-Mn complex 3olx 
Structural and functional effects of substitution at position T+1 in CheY: CheYA88S-BeF3-Mn complex 3oly 
Structural and functional effects of substitution at position T+1 in CheY: CheYA88M-BeF3-Mn complex 3oo0 
Structure of apo CheY A113P 3oo1 
Structure of E. Coli CheY mutant A113P in the absence of Sulfate 3q15 
Crystal Structure of RapH complexed with Spo0F 3q9s 
Crystal structure of rra(1-215) from Deinococcus Radiodurans 3r0j 
Structure of PhoP from Mycobacterium tuberculosis 3rqi 
Crystal structure of a response regulator protein from Burkholderia pseudomallei with a phosphorylated aspartic acid, calcium ion and citrate 3rvj 
Structure of the CheY-BeF3 Complex with substitutions at 59 and 89: N59D and E89Q 3rvk 
Structure of the CheY-Mn2+ Complex with substitutions at 59 and 89: N59D E89Q 3rvl 
Structure of the CheY-BeF3 Complex with substitutions at 59 and 89: N59D and E89R 3rvm 
Structure of the CheY-Mn2+ Complex with substitutions at 59 and 89: N59D and E89R 3rvn 
Structure of the CheY-BeF3 Complex with substitutions at 59 and 89: N59D and E89Y 3rvo 
Structure of CheY-Mn2+ Complex with substitutions at 59 and 89: N59D E89Y 3rvp 
Structure of the CheY-BeF3 Complex with substitutions at 59 and 89: N59D and E89K 3rvq 
Structure of the CheY-Mn2+ Complex with substitutions at 59 and 89: N59D E89K 3rvr 
Structure of the CheYN59D/E89R Molybdate complex 3rvs 
Structure of the CheYN59D/E89R Tungstate complex 3sy8 
Crystal structure of the response regulator RocR 3t6k 
Crystal structure of a Hypothetical RESPONSE REGULATOR (Caur_3799) from Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl at 1.86 A resolution 3t8y 
Crystal structure of the response regulator domain of Thermotoga maritima CheB 3tmy 
CHEY FROM THERMOTOGA MARITIMA (MN-III) 3to5 
High resolution structure of CheY3 from Vibrio cholerae 3w9s 
Crystal Structure Analysis of the N-terminal Receiver domain of Response Regulator PmrA 4b09 
Structure of unphosphorylated BaeR dimer 4cbv 
X-ray structure of full-length ComE from Streptococcus pneumoniae. 4d6x 
4D6X 4d6y 
4D6Y 4dad 
Crystal structure of a Putative pilus assembly-related protein (BPSS2195) from Burkholderia pseudomallei K96243 at 2.50 A resolution (PSI Community Target, Shapiro L.) 4dn6 
Crystal structure of a putative pilus assembly protein (cpaE) from Burkholderia thailandensis E264 at 2.80 A resolution 4e7o 
Crystal structure of receiver domain of putative NarL family response regulator spr1814 from Streptococcus pneumoniae 4e7p 
Crystal structure of receiver domain of putative NarL family response regulator spr1814 from Streptococcus pneumoniae in the presence of the phosphoryl analog beryllofluoride 4euk 
Crystal structure 4g97 
Crystal structure of the response regulator PhyR from Brucella abortus 4gvp 
Crystal Structure of the Response Regulator Protein VraR from Staphylococcus aureus 4h60 
High resolution structure of Vibrio cholerae chemotaxis protein CheY4 crystallized in low pH (4.0) condition 4hnq 
Crystal Structure of the mutant Q97A of Vibrio cholerae CheY3 4hnr 
High resolution structure of Chemotaxis response regulator CheY4 of Vibrio cholerae 4hns 
Crystal structure of activated CheY3 of Vibrio cholerae 4hye 
Crystal structure of a response regulator spr1814 from Streptococcus pneumoniae reveals unique interdomain contacts among NarL family proteins 4if4 
Crystal Structure of the Magnesium and beryllofluoride-activated VraR from Staphylococcus aureus 4iga 
The crystal structure of an activated Thermotoga maritima CheY with N-terminal region of FliM 4ja2 
Structural basis of a rationally rewired protein-protein interface (RR468mutant V13P, L14I, I17M and N21V) 4jas 
Structural basis of a rationally rewired protein-protein interface (HK853mutant A268V, A271G, T275M, V294T and D297E and RR468mutant V13P, L14I, I17M and N21V) 4jav 
Structural basis of a rationally rewired protein-protein interface (HK853wt and RR468mutant V13P, L14I, I17M and N21V) 4jp1 
Mg2+ bound structure of Vibrio Cholerae CheY3 4kfc 
Crystal structure of a hyperactive mutant of response regulator KdpE complexed to its promoter DNA 4kny 
Crystal structure of the response regulator KdpE complexed to DNA in an active-like conformation 4l4u 
Crystal structure of construct containing A. aeolicus NtrC1 receiver, central and DNA binding domains 4l85 
Crystal structure of receiver domain of KdpE D52A mutant from E. coli 4ldz 
4LDZ 4le0 
4LE0 4le1 
4LE1 4le2 
4LE2 4lx8 
Crystal structure (2.2A) of Mg2+ bound CheY3 of Vibrio cholerae 4lzl 
4LZL 4ml3 
X-ray structure of ComE D58A REC domain from Streptococcus pneumoniae 4mld 
X-ray structure of ComE D58E REC domain from Streptococcus pneumoniae 4myr 
Crystal structure of a putative CpaE2 pilus assembly protein (CpaE2) from Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 at 2.72 A resolution (PSI Community Target, Shapiro) 4nic 
4NIC 4q7e 
Non-phosphorylated HemR Receiver Domain from Leptospira biflexa 4qic 
4QIC 4qpj 
4QPJ 4qwv 
4QWV 4qyw 
4QYW 4s04 
4S04 4s05 
4S05 4tmy 
CHEY FROM THERMOTOGA MARITIMA (MG-IV) 4uhj 
4UHJ 4uhk 
4UHK 4uhs 
4UHS 4xlt 
4XLT 4yn8 
4YN8 4zmr 
4ZMR 4zms 
4ZMS 4zyl 
4ZYL 5brj 
5BRJ 5chy 
STRUCTURE OF CHEMOTAXIS PROTEIN CHEY 5d2c 
5D2C 5dcl 
5DCL 5dcm 
5DCM 5dgc 
5DGC 5dkf 
5DKF 5e3j 
5E3J 5ed4 
5ED4 5ep0 
5EP0 5f64 
5F64 5hev 
5HEV 5i4c 
5I4C 5ic5 
5IC5 5ieb 
5IEB 5iej 
5IEJ 5t3y 
5T3Y 5te9 
5TE9 5tqj 
5TQJ 6chy 
STRUCTURE OF CHEMOTAXIS PROTEIN CHEY - Links (links to other resources describing this domain)
-
INTERPRO IPR001789 PFAM response_reg

