Version history
Changes from version 9.0 to 10.0
- SMART's web user interface has been modernized and completely rewritten from scratch
- Multiple copies of SMART and Pfam domains can be included in the architecture queries
- Architecture SMART queries are much faster now, with instant display of the proteins selected
- Updated functionality of the protein schematic display applet, which remains on the screen when the page is scrolled, and scrolls automatically to any selected feature
- Pathways links have been updated with full support for version 3 of the interactive Pathways Explorer
- Improved display of protein interaction networks from STRING, which can be navigated and their members selected directly in SMART
- Updated orthology information, with links to the current release of eggNOG (v6)
Changes from version 8.0 to 9.0
- Completely rewritten protein schematic display applet, providing widest possible browser support.
- Architecture data export and visualization in iTOL optimized for current iTOL version (v5)
- Updated full text search engine
Changes from version 7.0 to 8.0
- Vector based protein schematic display applet, allowing lossless zooming and export to bitmap and vector graphical formats.
- SVG based protein display in architecture analysis results displays
- Architecture data export and visualization in iTOL version 3
- Updated full text search engine
- New taxonomic data tree display, with increased speed and full text local search
Changes from version 6.0 to 7.0
- Full text search engine
Use the box in the top right corner of any page to perform a full text search of SMART and Pfam domain annotations, p lus the complete protein descriptions for Uniprot and Ensembl proteins - metaSMART
Explore and compare domain architectures in various publicly available metagenomics datasets. - iTOL export and visualization
Domain architecture analysis results can be exported and visualized in interactive Tree Of Life. New option can be found in the protein list function select list. - User interface cleanup
Various small changes to the UI, resulting in faster and easier navigation
Changes from version 5.1 to 6.0
- Metabolic pathways information
SMART domains and proteins available in the "genomic" mode now have basic metabolic pathways information. It is generated by mapping our genomic mode protein database to the KEGG orthologous groups. - Updated genomic mode protein database
Greatly expanded genomic mode database now includes sequences from 630 completely sequences species.
Changes from version 5.0 to 5.1
- SMART webservice
You can access SMART using our webservice. Check the WSDL file for details. The webservice is still under active development and only works for sequences and IDs which are in our database (complete Uniref100 and stable Ensembl genomes). - SMART DAS server
SMART DAS server is available at URL http://smart.embl.de/smart/das. It provides all the protein features from our database (SMART domains, signal peptides, transmembrane regions and coiled coils) for all Uniref100 and Ensembl proteins.
Changes from version 4.1 to 5.0
- New protein database in 'Normal' mode
SMART now uses Uniprot as the main source of protein sequences. All Ensembl proteomes (except pre-releases) are also included. To lower redundancy in the database, the following procedure is used:- only one copy of 100% identical proteins is kept (different IDs are still available)
- each species' proteins are separated
- CD-HIT clustering with 96% identity cutoff is preformed on each species separately
- longest member of each protein cluster is used as the representative
- only representative cluster members and single proteins (ie. proteins which are not members of any clusters) are used in all domain architecture queries and for domain counts in the annotation pages
- Domain architecture invention dating
As a further step from the single domain to the understanding of multi domain proteins, SMART now predicts the taxonomic class, where the concept of a protein, that is its domain architecture, was invented. The domain architecture is defined as the linear order of all SMART domains in the protein sequence. To derive the point of its invention, all proteins with the same domain architecture are mapped onto NCBIs taxonomy . The last common ancestor of all organisms containing at least one protein with the domain architecture is defined as the point of its origin.
Changes from version 4.0 to 4.1
- Two modes of operation: Normal and Genomic
For more details, visit the change mode page. - Intrinsic protein disorder prediction
You can now include DisEMBL prediction of protein disorder in your search parameters. The results are displayed as blue regions in protein schematics. DisEMBL's HOTLOOPS and REM465 methods are currently used. Visit the DisEMBL page for more information on the method. - Catalytic activity check
SMART now includes data on specific requirements for catalytic activity for some of our domains (50 catalytic domains at the moment, full list here). If the required amino acids are not present in the predicted domain, it will be marked as 'Inactive'. Domain annotation page will show you the details on which amino acids are missing and the links to relevant literature. Pubmed link - Taxonomic trees
Architecture query results are now displayed as simple taxonomic trees. In addition to individual proteins, you can select any taxonomic node (or multiple nodes) and display all the proteins in those nodes.
The 'Evolution' section of domain annotation pages is now also represented as a taxonomic tree. The basic tree contains only several hand-picked, representative species, with a link to the full tree. - User interface redesigned
SMART has been completely rewriten, and all pages are conforming to the XHTML 1.0 Strict and CSS Level 2 standards. We recommend a modern, standards compliant browser for the best experience. Mozilla Firefox and Opera are our favorites.
Changes from version 3.5 to 4.0
- Intron positions are shown in protein schematics
For proteins that match any of the Ensembl predictions, SMART will show intron positions as vertical coloured lines in graphical representations (see example). This information is retrieved from a pre-calculated mapping of Ensembl gene structures to protein sequences.
Vertical line at the end of the protein is not an actual intron, but a mark to show that intron mapping was performed. If that is the only line, there are no introns annotated. If there is no line at all, there is no data avaliable in Ensembl for that particular sequence.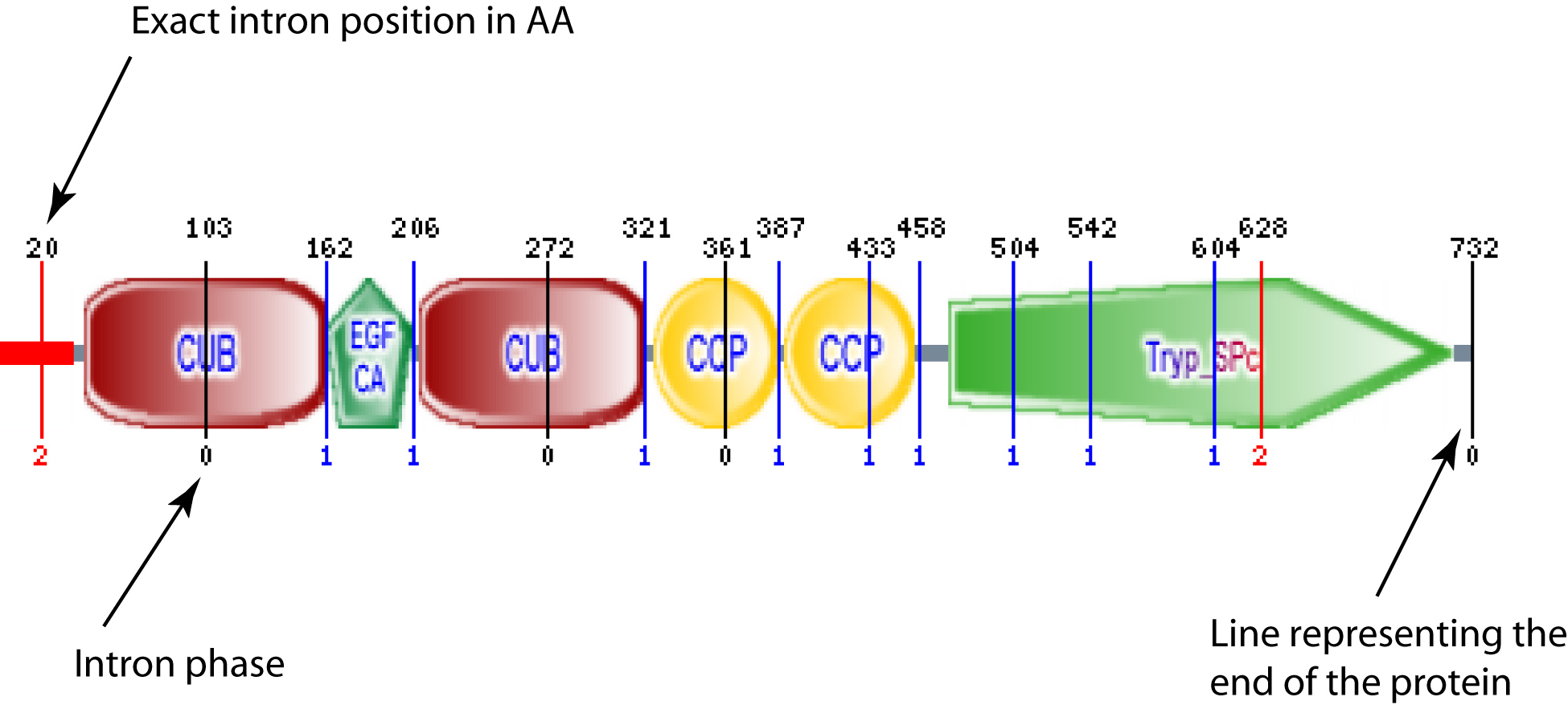
You can switch off intron display on your SMART preferences page.
- Alternative splicing information
Since SMART now incorporates Ensembl genomes, 'Additional information' page shows a list of alternative splices of the gene encoding the analyzed protein (if there are any). It is possible to either display SMART protein annotation for any of the alternative splices, or get a graphical multiple sequence alignment of all of them. - Orthology information
There are 2 separate sets of orthologs for each Ensembl protein: 1:1 reciprocal best matches in other genomes and orthologous groups with reciprocal best hits from all genomes analyzed (i.e. each of these proteins has exactly one ortholog in all 6 genomes).
This data is displayed on 'Additional information' page. - Graphical multiple sequence alignments
Orthologus groups and different aliternative splices can be displayed as graphical multiple sequence alignments. Proteins are aligned using ClustalW. Domains, intrinsic features and introns are mapped onto the alignment with their positions adjusted according to gaps (black boxes).
Changes from version 3.4 to 3.5
- Features of all Ensembl genomes are stored in SMART
You can use standard Ensembl protein identifiers (for example, ENSP00000264122) and sequences in all queries. - Batch access
Quickly display results for hundreds of sequences. Currently limited to 500 sequences per access, 2000 per day. - Smarter handling of identical sequences
If there are multiple IDs associated with a particular sequence, an extra table will be displayed showing all of them.
Changes from version 3.3 to 3.4
- Search structure based profiles using RPS-Blast
Clicking on the search schnipsel and structures checkbox will now also initiate a search of profiles based on scop domain families, using RPS-Blast. These profiles were kindly provided by Steffen Schmidt (see Schmidt et al. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2002 (42) 405-7). - Improved Architecture analysis
In addition to standard 'Domain selection' querying, it is now possible to do queries based on GO (Gene ontology, click here for more info) terms associated with domains. In the first step, you get a list of domains matching the GO terms entered. After selecting the domains of interest from the list, proteins containing those domains are displayed. Use 'Taxonomic selection' box to limit the results based on taxonomic ranges. - Pfam domains are stored in the database
SMART database now contains precomputed results for all Pfam domains. To use Pfam domains in the architecture queries, prepend the domain name with 'Pfam:' (for example, "TyrKc AND Pfam:Fz AND TRANS") - Try our SMART Toolbar for Mozilla web browser! Click here for more info.
Changes from version 3.2 to 3.3
- Fantastic new protein picture generator
Proteins are now displayed as dynamically generated PNG images. This means that you can download the entire protein representation as a single image. You have our permission to do this and use these diagrams in any way that you like; do acknowledge us though. All domain bubbles have been script-generated using The Gimp and it's Perl-Fu extension. The script is GPL'd and is avaliable for download - Fancy colour alignments
All alignments we generate are coloured in using Leo Goodstadt's excellent CHROMA program. CHROMA is available from here and it's great. You may experience some problems if you're using a klunky browser. This will be fixed when you change your browser. - Excellent transmembrane domains
These are now calculated using the fine TMHMM2 program (the main web site is here ), kindly provided by Anders Krogh and co-workers. You can read about the method here . - Selective SMART
We now store intrinsic features such as transmembrane domains, and signal peptides in our database. This means that these can be queried for (e.g. SIGNAL AND TyrKc). The feature names are Signal peptide: SIGNAL, transmembrane domain: TRANS, coiled-coli COIL. - Techincal changes
SMART code has been modified to run under Apache mod_perl module. SMART is now using Apache::DBI for persistent database connections. Database engine has been updated to the PostgreSQL 7.1. These changes resulted in significant speed improvements. - Bug fixes as usual...
show_many_proteins script now uses POST method, so there is no longer a limit on number of proteins you can display. Fixed a display problem with proteins having thousands of different representations (if you try to display those, make sure you have a good browser (like Mozilla or Opera :-) and a bunch of RAM).
Changes from version 3.1 to 3.2
- Start page
There is an indicator of the current database status in the header now... If the database is down or is being updated you'll know immediately. - Literature
Changed literature identifiers to PMID. New secondary literature generator that parses all neigbouring papers, not just first 100. - Numerous small bug fixes and improvements...
Changes from version 3.0 to 3.1
- Startup page
The start page now includes selective SMART and allows to search for keywords in the annotation of domains. - Schnipsel Blast
The results of a schnipsel Blast search are included into the bubble diagramm. Additionally, PDB is searched. - Taxonomic breakdown
When selecting multiple proteins, e.g. via selective SMART or the annotation pages, an overview of the taxonomy of all species (tax break) is offered. - Links
Links don't contain version numbers. This allows stable links from external sources. - Selective SMART
Allows to search for multiple copies of domains and is case insensitive. You can now search for e.g. 'Sh3 AND sH3 AND sh3' - Annotation
You can align youre query sequence to the SMART alignment using hmmalign - Update of underlying database
SMART now uses PostgreSQL 6.5.2.
Changes from version 2.0 to 3.0
- Digest output
SMART now only produces a single diagram representing a 'best' interpretation of all the annotation that has been performed. A comprehensive summary of the results is also provided in table format. - selective SMART
Selective SMART allows to look for proteins with combinations of specific domains in different species or taxonomic ranges. - alert SMART
The SMART database gets updated about once a week. If you are interested in specific domains or combination of them in specific taxonomic ranges, you can use the SMART alerting service. This provides the identities of newly-deposited proteins that match your query. - Domain queries
You can ask for proteins having the same domain order / composition as your query protein. - SMARTed Genomes
You can get the result of SMARTing the genomes of Caenorhabditis elegans and Saccharomyces cerevisiae via the annotation pages. - Faster PFAM searches
The PFAM searches now runs on a PVM cluster.
Changes from version 1.03 to 2.0
- Domain coverage
The original set of signalling domains has now been extended to include extracellular domains. - Default search method is now HMMer
The previously-used underlying methodology of SMART (i.e. SWise) tended to over-extend gaps, leading to problems in defining domain borders. Although a SWise search of the SMART database remains possible (using the 'Wise searching SMART database' option available from the Home Page) the default searching method is now HMMer2. This now allows improved statistical estimates ("Expectation- or E-values) of the significance of a domain hit. - Complete rewrite of the annotation pages
As with the previous version (1.03), annotation pages provide information concerning domain functions, and include hyperlinks to PubMed. However, we now offer automatically-derived data showing the taxonomic range and the predicted cellular localisation of proteins containing the domain in question. - Literature database
In addition to the manual derived literature sources given in version 1.03, we now provide automatically-derived 'secondary' literature from the annotation pages. These are extracted from PubMed and are cross-linked to additional abstracts.