The domain within your query sequence starts at position 923 and ends at position 1002; the E-value for the FN3 domain shown below is 5.53e-4.
PDPVQESSFRIEGHTSSFQILWNEPPAVDWGIVFYSVEFSTHSKFLIIEQQSLPIFTVEG LEPYTLFNLSVTPYTYWGKG
FN3Fibronectin type 3 domain |
|---|
| SMART accession number: | SM00060 |
|---|---|
| Description: | One of three types of internal repeat within the plasma protein, fibronectin. The tenth fibronectin type III repeat contains a RGD cell recognition sequence in a flexible loop between 2 strands. Type III modules are present in both extracellular and intracellular proteins. |
| Interpro abstract (IPR003961): | Fibronectin is a dimeric glycoprotein composed of disulfide-linked subunits with a molecular weight of 220-250kDa each. It is involved in cell adhesion, cell morphology, thrombosis, cell migration, and embryonic differentiation. Fibronectin is a modular protein composed of homologous repeats of three prototypical types of domains known as types I, II, and III [ (PUBMED:6218503) ]. Fibronectin type-III (FN3) repeats are both the largest and the most common of the fibronectin subdomains. Domains homologous to FN3 repeats have been found in various animal protein families including other extracellular-matrix molecules, cell-surface receptors, enzymes, and muscle proteins [ (PUBMED:1409594) ]. Structures of individual FN3 domains have revealed a conserved beta sandwich fold with one beta sheet containing four strands and the other sheet containing three strands (see for example {PDB:1TEN}) [ (PUBMED:1279805) ]. This fold is topologically very similar to that of Ig-like domains, with a notable difference being the lack of a conserved disulfide bond in FN3 domains. Distinctive hydrophobic core packing and the lack of detectable sequence homology between immunoglobulin and FN3 domains suggest, however, that these domains are not evolutionarily related [ (PUBMED:1279805) ]. FN3 exhibits functional as well as structural modularity. Sites of interaction with other molecules have been mapped to short stretch of amino acids such as the Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) sequence found in various FN3 domains. The RGD sequences is involved in interactions with integrin. Small peptides containing the RGD sequence can modulate a variety of cell adhesion invents associated with thrombosis, inflammation, and tumor metastasis. These properties have led to the investigation of RGD peptides and RGD peptide analogs as potential therapeutic agents [ (PUBMED:8548820) ]. |
| GO function: | protein binding (GO:0005515) |
| Family alignment: |
There are 647694 FN3 domains in 183810 proteins in SMART's nrdb database.
Click on the following links for more information.
- Evolution (species in which this domain is found)
-
Taxonomic distribution of proteins containing FN3 domain.
This tree includes only several representative species. The complete taxonomic breakdown of all proteins with FN3 domain is also avaliable.
Click on the protein counts, or double click on taxonomic names to display all proteins containing FN3 domain in the selected taxonomic class.
- Literature (relevant references for this domain)
-
Primary literature is listed below; Automatically-derived, secondary literature is also avaliable.
- Leahy DJ, Aukhil I, Erickson HP
- 2.0 A crystal structure of a four-domain segment of human fibronectin encompassing the RGD loop and synergy region.
- Cell. 1996; 84: 155-64
- Display abstract
We have determined the 2.0 A crystal structure of a fragment of human fibronectin encompassing the seventh through the RGD-containing tenth type III repeats (FN7-10). The structure reveals an extended rod-like molecule with a long axis of approximately 140 A and highly variable relationships between adjacent domains. An unusually small rotation between domains 9 and 10 creates a distinctive binding site, in which the RGD loop from domain 10 and the "synergy" region from domain 9 are on the same face of FN7-10 and thus easily accessible to a single integrin molecule. The cell-binding RGD loop is well-ordered in this structure and extends approximately 10 A away from the FN7-10 core.
- Huber AH, Wang YM, Bieber AJ, Bjorkman PJ
- Crystal structure of tandem type III fibronectin domains from Drosophila neuroglian at 2.0 A.
- Neuron. 1994; 12: 717-31
- Display abstract
We report the crystal structure of two adjacent fibronectin type III repeats from the Drosophila neural cell adhesion molecule neuroglian. Each domain consists of two antiparallel beta sheets and is folded topologically identically to single fibronectin type III domains from the extracellular matrix proteins tenascin and fibronectin. beta bulges and left-handed polyproline II helices disrupt the regular beta sheet structure of both neuroglian domains. The hydrophobic interdomain interface includes a metal-binding site, presumably involved in stabilizing the relative orientation between domains and predicted by sequence comparision to be present in the vertebrate homolog molecule L1. The neuroglian domains are related by a near perfect 2-fold screw axis along the longest molecular dimension. Using this relationship, a model for arrays of tandem fibronectin type III repeats in neuroglian and other molecules is proposed.
- Potts JR, Campbell ID
- Fibronectin structure and assembly.
- Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994; 6: 648-55
- Display abstract
Significant progress has been made recently in the determination of the structure and assembly of the important matrix protein fibronectin, a molecule mainly constructed from three modular units denoted Fn1, Fn2 and Fn3. Atomic resolution structures are now available for all three single modules, for Fn1 and Fn3 module pairs, and for the disulphide-linked join between fibronectin monomers. Combined with results from new binding and mutation studies, the new structural information is leading to a clearer view of structure/function relationships in intact fibronectin.
- Skorstengaard K, Holtet TL, Etzerodt M, Thogersen HC
- Collagen-binding recombinant fibronectin fragments containing type II domains.
- FEBS Lett. 1994; 343: 47-50
- Display abstract
Each of the two type II domains and four larger fragments, containing one or two type II domains of fibronectin, have been expressed in Escherichia coli. A special vector, containing a fragment encoding the cleavage site for Factor Xa, Ile-Glu-Gly-Arg, inserted immediately before the protein fragment of interest, was used. After treatment of the purified fusion proteins with reduced/oxidized glutathione, the correctly folded fibronectin fragments were released by proteolytic digestion with Factor Xa. The largest fragment, consisting of two type II and two type I domains, was the only fragment able to bind to immobilized gelatin.
- Leahy DJ, Hendrickson WA, Aukhil I, Erickson HP
- Structure of a fibronectin type III domain from tenascin phased by MAD analysis of the selenomethionyl protein.
- Science. 1992; 258: 987-91
- Display abstract
Fibronectin type III domains are found in many different proteins including cell surface receptors and cell adhesion molecules. The crystal structure of one such domain from the extracellular matrix protein tenascin was determined. The structure was solved by multiwavelength anomalous diffraction (MAD) phasing of the selenomethionyl protein and has been refined to 1.8 angstrom resolution. The folding topology of this domain is identical to that of the extracellular domains of the human growth hormone receptor, the second domain of CD4, and PapD. Although distinct, this topology is similar to that of immunoglobulin constant domains. An Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) sequence that can function for cell adhesion is found in a tight turn on an exposed loop.
- Main AL, Harvey TS, Baron M, Boyd J, Campbell ID
- The three-dimensional structure of the tenth type III module of fibronectin: an insight into RGD-mediated interactions.
- Cell. 1992; 71: 671-8
- Display abstract
The solution structure of the tenth type III module of fibronectin has been determined using nuclear magnetic resonance techniques. The molecule has a fold similar to that of immunoglobulin domains, with seven beta strands forming two antiparallel beta sheets, which pack against each other. Both beta sheets contribute conserved hydrophobic residues to a compact core. The topology is more similar to that of domain 2 of CD4, PapD, and the extracellular domain of the human growth hormone receptor than to that of immunoglobulin C domains. The module contains an Arg-Gly-Asp sequence known to be involved in cell adhesion. This tripeptide is solvent exposed and lies on a conformationally mobile loop between strands F and G, consistent with its cell adhesion function.
- Petersen TE et al.
- Partial primary structure of bovine plasma fibronectin: three types of internal homology.
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983; 80: 137-41
- Balian G, Click EM, Bornstein P
- Location of a collagen-binding domain in fibronectin.
- J Biol Chem. 1980; 255: 3234-6
- Display abstract
Preferential labeling of COOH-terminal sequences in newly synthesized fibronectin was achieved by short term incorporation of radiolabeled amino acids in the presence of pactamycin, an inhibitor of polypeptide chain initiation. The labeled fibronectin was then cleaved with cathepsin D under conditions that yield a large (137,000-dalton) fragment that lacks collagen-binding properties, and a smaller (72,000-dalton) fragment that retains the ability of fibronectin to bind to collagen. Determination of the relative specific radioactivities of the two fragments leads us to conclude that the collagen-binding domain in fibronectin is located in the NH2-terminal third of the polypeptide chain and not in a COOH-terminal region as previously indicated by other structural studies.
- Disease (disease genes where sequence variants are found in this domain)
-
SwissProt sequences and OMIM curated human diseases associated with missense mutations within the FN3 domain.
Protein Disease Anosmin-1 (P23352) (SMART) OMIM:308700: Kallmann syndrome Neural cell adhesion molecule L1 (P32004) (SMART) OMIM:308840: Hydrocephalus due to aqueductal stenosis
OMIM:307000: MASA syndrome
OMIM:303350: Spastic paraplegia
OMIM:312900:Collagen alpha-1(VII) chain (Q02388) (SMART) OMIM:120120: Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica, dominant
OMIM:131750: Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica, recessive
OMIM:226600: Epidermolysis bullosa, pretibial, dominant and recessive
OMIM:131850:Leptin receptor (P48357) (SMART) OMIM:601007: LEPTIN RECEPTOR; LEPR Cytokine receptor common subunit gamma (P31785) (SMART) OMIM:308380: Severe combined immunodeficiency, X-linked
OMIM:300400: Combined immunodeficiency, X-linked, moderate
OMIM:312863:Integrin beta-4 (P16144) (SMART) OMIM:147557: Epidermolysis bullosa, junctional, with pyloric atresia
OMIM:226730: Epidermolysis bullosa, generalized atrophic benign
OMIM:226650:Insulin receptor (P06213) (SMART) OMIM:147670: Leprechaunism
OMIM:246200: Rabson-Mendenhall syndrome
OMIM:262190: Diabetes mellitus, insulin-resistant, with acanthosis nigricans - Metabolism (metabolic pathways involving proteins which contain this domain)
-
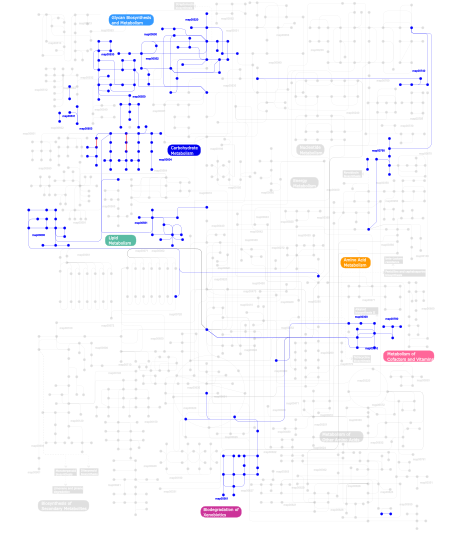
Click the image to view the interactive version of the map in iPath% proteins involved KEGG pathway ID Description 21.19 map04060 Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction 13.17 map04360 Axon guidance 8.71 map04514 Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) 7.56 map04510 Focal adhesion 5.15 map04512 ECM-receptor interaction 5.15 map04640 Hematopoietic cell lineage 4.81 map04520 Adherens junction 3.21 map04810 Regulation of actin cytoskeleton 2.75  map00530
map00530Aminosugars metabolism 2.63 map04080 Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction 1.72 map05210 Colorectal cancer 1.72 map04650 Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity 1.60 map04910 Insulin signaling pathway 1.60 map05215 Prostate cancer 1.15 map05214 Glioma 1.15 map04620 Toll-like receptor signaling pathway 1.15 map04730 Long-term depression 1.15 map05218 Melanoma 1.15 map04914 Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation 1.03 map04920 Adipocytokine signaling pathway 1.03 map04020 Calcium signaling pathway 0.92 map05222 Small cell lung cancer 0.92 map05120 Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection 0.92 map05050 Dentatorubropallidoluysian atrophy (DRPLA) 0.92 map04210 Apoptosis 0.92 map04930 Type II diabetes mellitus 0.80 map04120 Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis 0.80 map04660 T cell receptor signaling pathway 0.57  map00500
map00500Starch and sucrose metabolism 0.46  map00361
map00361gamma-Hexachlorocyclohexane degradation 0.34 map04740 Olfactory transduction 0.34  map00790
map00790Folate biosynthesis 0.34 map02020 Two-component system - General 0.34 map00511 N-Glycan degradation 0.34 map01032 Glycan structures - degradation 0.23  map00531
map00531Glycosaminoglycan degradation 0.23 map04010 MAPK signaling pathway 0.23 map04940 Type I diabetes mellitus 0.23  map00604
map00604Glycosphingolipid biosynthesis - ganglioseries 0.23  map00600
map00600Sphingolipid metabolism 0.11  map00603
map00603Glycosphingolipid biosynthesis - globoseries 0.11  map00780
map00780Biotin metabolism 0.11  map00740
map00740Riboflavin metabolism 0.11  map00300
map00300Lysine biosynthesis 0.11  map00310
map00310Lysine degradation 0.11  map00561
map00561Glycerolipid metabolism 0.11  map00052
map00052Galactose metabolism 0.11 map02010 ABC transporters - General 0.11  map00520
map00520Nucleotide sugars metabolism 0.11  map00550
map00550Peptidoglycan biosynthesis This information is based on mapping of SMART genomic protein database to KEGG orthologous groups. Percentage points are related to the number of proteins with FN3 domain which could be assigned to a KEGG orthologous group, and not all proteins containing FN3 domain. Please note that proteins can be included in multiple pathways, ie. the numbers above will not always add up to 100%.
- Structure (3D structures containing this domain)
3D Structures of FN3 domains in PDB
PDB code Main view Title 1a22 
HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE BOUND TO SINGLE RECEPTOR 1axi 
STRUCTURAL PLASTICITY AT THE HGH:HGHBP INTERFACE 1bj8 
THIRD N-TERMINAL DOMAIN OF GP130, NMR, MINIMIZED AVERAGE STRUCTURE 1bp3 
THE XRAY STRUCTURE OF A GROWTH HORMONE-PROLACTIN RECEPTOR COMPLEX 1bpv 
TITIN MODULE A71 FROM HUMAN CARDIAC MUSCLE, NMR, 50 STRUCTURES 1bqu 
CYTOKYNE-BINDING REGION OF GP130 1c8p 
NMR STRUCTURE OF THE LIGAND BINDING DOMAIN OF THE COMMON BETA-CHAIN IN THE GM-CSF, IL-3 AND IL-5 RECEPTORS 1cfb 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF TANDEM TYPE III FIBRONECTIN DOMAINS FROM DROSOPHILA NEUROGLIAN AT 2.0 ANGSTROMS 1cn4 
ERYTHROPOIETIN COMPLEXED WITH EXTRACELLULAR DOMAINS OF ERYTHROPOIETIN RECEPTOR 1eba 
COMPLEX BETWEEN THE EXTRACELLULAR DOMAIN OF ERYTHROPOIETIN (EPO) RECEPTOR [EBP] AND AN INACTIVE PEPTIDE [EMP33] CONTAINS 3,5-DIBROMOTYROSINE IN POSITION 4 (DENOTED DBY) 1ebp 
COMPLEX BETWEEN THE EXTRACELLULAR DOMAIN OF ERYTHROPOIETIN (EPO) RECEPTOR [EBP] AND AN AGONIST PEPTIDE [EMP1] 1eer 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN ERYTHROPOIETIN COMPLEXED TO ITS RECEPTOR AT 1.9 ANGSTROMS 1egj 
DOMAIN 4 OF THE BETA COMMON CHAIN IN COMPLEX WITH AN ANTIBODY 1ern 
NATIVE STRUCTURE OF THE EXTRACELLULAR DOMAIN OF ERYTHROPOIETIN (EPO) RECEPTOR [EBP] 1f6f 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE TERNARY COMPLEX BETWEEN OVINE PLACENTAL LACTOGEN AND THE EXTRACELLULAR DOMAIN OF THE RAT PROLACTIN RECEPTOR 1fna 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE TENTH TYPE III CELL ADHESION MODULE OF HUMAN FIBRONECTIN 1fnf 
FRAGMENT OF HUMAN FIBRONECTIN ENCOMPASSING TYPE-III REPEATS 7 THROUGH 10 1fnh 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HEPARIN AND INTEGRIN BINDING SEGMENT OF HUMAN FIBRONECTIN 1gh7 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE COMPLETE EXTRACELLULAR DOMAIN OF THE BETA-COMMON RECEPTOR OF IL-3, IL-5, AND GM-CSF 1hwg 
1:2 COMPLEX OF HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE WITH ITS SOLUBLE BINDING PROTEIN 1hwh 
1:1 COMPLEX OF HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE MUTANT G120R WITH ITS SOLUBLE BINDING PROTEIN 1i1r 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A CYTOKINE/RECEPTOR COMPLEX 1iar 
INTERLEUKIN-4 / RECEPTOR ALPHA CHAIN COMPLEX 1j8k 
NMR STRUCTURE OF THE FIBRONECTIN EDA DOMAIN, NMR, 20 STRUCTURES 1k85 
Solution structure of the fibronectin type III domain from Bacillus circulans WL-12 Chitinase A1. 1kf9 
PHAGE DISPLAY DERIVED VARIANT OF HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE COMPLEXED WITH TWO COPIES OF THE EXTRACELLULAR DOMAIN OF ITS RECEPTOR 1lwr 
Solution structure of the NCAM fibronectin type III module 2 1mfn 
SOLUTION NMR STRUCTURE OF LINKED CELL ATTACHMENT MODULES OF MOUSE FIBRONECTIN CONTAINING THE RGD AND SYNERGY REGIONS, 20 STRUCTURES 1n26 
Crystal Structure of the extra-cellular domains of Human Interleukin-6 Receptor alpha chain 1oww 
Solution structure of the first type III module of human fibronectin determined by 1H, 15N NMR spectroscopy 1p9m 
Crystal structure of the hexameric human IL-6/IL-6 alpha receptor/gp130 complex 1pvh 
Crystal structure of leukemia inhibitory factor in complex with gp130 1qg3 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A TANDEM PAIR OF FIBRONECTIN TYPE III DOMAINS FROM THE CYTOPLASMIC TAIL OF INTEGRIN ALPHA6 BETA4 1qr4 
TWO FIBRONECTIN TYPE-III DOMAIN SEGMENT FROM CHICKEN TENASCIN 1tdq 
Structural basis for the interactions between tenascins and the C-type lectin domains from lecticans: evidence for a cross-linking role for tenascins 1ten 
STRUCTURE OF A FIBRONECTIN TYPE III DOMAIN FROM TENASCIN PHASED BY MAD ANALYSIS OF THE SELENOMETHIONYL PROTEIN 1ttf 
THE THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF THE TENTH TYPE III MODULE OF FIBRONECTIN: AN INSIGHT INTO RGD-MEDIATED INTERACTIONS 1ttg 
THE THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF THE TENTH TYPE III MODULE OF FIBRONECTIN: AN INSIGHT INTO RGD-MEDIATED INTERACTIONS 1uc6 
Solution Structure of the Carboxyl Terminal Domain of the Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor Receptor 1uem 
Solution Structure of the First Fibronectin Type III domain of human KIAA1568 Protein 1uen 
Solution Structure of The Third Fibronectin III Domain of Human KIAA0343 Protein 1uey 
Solution Structure of The First Fibronectin Type III Domain of Human KIAA0343 protein 1ujt 
Solution structure of the second fibronectin Type III domain of human KIAA1568 protein 1v5j 
Solution Structure of RSGI RUH-008, fn3 domain in Human cDNA 1va9 
Solution structure of the second FNIII domain of DSCAML1 protein 1wf5 
Solution structure of the first Fn3 domain of Sidekick-2 protein 1wfn 
The fourth FN3 domain of human sidekick-2 1wfo 
The eighth FN3 domain of human sidekick-2 1wft 
Solution structure of C-terminal fibronectin type III domain of mouse 1700129L13Rik protein 1wfu 
Solution structure of fibronectin type III domain of mouse hypothetical protein 1wis 
Solution structure of the fifth FNIII domain from human KIAA1514 protein 1wj3 
Solution structure of the fourth fn3 domain of KIAA1496 protein 1wk0 
Solution structure of Fibronectin type III domain derived from human KIAA0970 protein 1x3d 
Solution structure of the fibronectin type-III domain of human fibronectin type-III domain containing protein 3a 1x4x 
Solution structure of the 6th fibronectin type III domain from human fibronectin type III domain containing protein 3 1x4y 
Solution structure of the 3rd fibronectin type III domain from mouse biregional cell adhesion molecule-related/down-regulated oncogenes (Cdon) binding protein 1x4z 
Solution structure of the 2nd fibronectin type III domain from mouse biregional cell adhesion molecule-related/down-regulated oncogenes (Cdon) binding protein 1x5a 
The solution structure of the second fibronectin type III domain of mouse Ephrin type-A receptor 1 1x5f 
The solution structure of the first fibronectin type III domain of human Neogenin 1x5g 
The solution structure of the second fibronectin type III domain of human Neogenin 1x5h 
The solution structure of the third fibronectin type III domain of human Neogenin 1x5i 
The solution structure of the fourth fibronectin type III domain of human Neogenin 1x5j 
The solution structure of the fifth fibronectin type III domain of human Neogenin 1x5k 
The solution structure of the sixth fibronectin type III domain of human Neogenin 1x5l 
Solution structure of the second fn3 domain of Eph receptor A8 protein 1x5x 
Solution structure of the fibronectin type-III domain of human fibronectin type III domain containing protein 3 1x5y 
Solution structure of the fibronectin type-III domain of mouse myosin-binding protein C, Fast-type homolog 1x5z 
Solution structure of the fibronectin type-III domain of human protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, D isoform 4 variant 1zlg 
Solution structure of the extracellular matrix protein anosmin-1 2aew 
A model for growth hormone receptor activation based on subunit rotation within a receptor dimer 2arw 
The solution structure of the membrane proximal cytokine receptor domain of the human interleukin-6 receptor 2b5i 
cytokine receptor complex 2ck2 
Structure of core-swapped mutant of fibronectin 2crm 
Solution structure of the forth FNIII domain of human 2crz 
Solution structure of the fifth FNIII domain of human fibronectin type III domain containing protein 3a 2csp 
Solution structure of the FNIII domain of human RIM-binding protein 2 2cuh 
Solution structure of the 31st fibronectin type III domain of the human tenascin X 2cui 
Solution structure of the 31st fibronectin type III domain of the human tenascin X 2cum 
The solution structure of the 33rd fibronectin type III domain of human Tenascin-X 2d9q 
Crystal Structure of the Human GCSF-Receptor Signaling Complex 2db8 
Solution structures of the fn3 domain of human Tripartite motif protein 9 2dbj 
Solution structures of the fn3 domain of human Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase MER precursor 2djs 
Solution structures of the fn3 domain of human ephrin type-B receptor 1 2dju 
Solution structures of the fn3 domain of human receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase F 2dkm 
Solution structures of the fn3 domain of human collagen alpha-1(XX) chain 2dle 
Solution structure of the fourth fn3 domain of human receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase eta 2dlh 
Solution structure of the second fn3 domain of human receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase delta 2dm4 
Solution structure of the second fn3 domain of human sorLA/LR11 2dmk 
The solution structure of the FN3 domain of human Midline 2 protein 2dn7 
Solution structures of the 6th fn3 domain of human receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase F 2doc 
Solution structure of the Fibronectin type-III domain of human Neural cell adhesion molecule 2 2e3v 
Crystal structure of the first fibronectin type III domain of neural cell adhesion molecule splicing isoform from human muscle culture lambda-4.4 2e7h 
Solution structure of the second fn3 domain from human Ephrin type-B receptor 4 2ed7 
Solution structure of the first fibronectin type III domain of human Netrin receptor DCC 2ed8 
Solution structure of the second fibronectin type III domain of human Netrin receptor DCC 2ed9 
Solution structure of the third fibronectin type III domain of human Netrin receptor DCC 2edb 
Solution structure of the fourth fibronectin type III domain of human Netrin receptor DCC 2edd 
Solution structure of the fifth fibronectin type III domain of human Netrin receptor DCC 2ede 
Solution structure of the sixth fibronectin type III domain of human Netrin receptor DCC 2edx 
Solution structures of the fn3 domain of human receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase F 2edy 
Solution structures of the fn3 domain of human receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase F 2ee2 
Solution structures of the fn3 domain of human contactin 1 2ee3 
Solution structures of the fn3 domain of human collagen alpha-1(XX) chain 2ekj 
Solution structures of the fn3 domain of human collagen alpha-1(XX) chain 2erj 
Crystal structure of the heterotrimeric interleukin-2 receptor in complex with interleukin-2 2fnb 
NMR STRUCTURE OF THE FIBRONECTIN ED-B DOMAIN, NMR, 20 STRUCTURES 2gee 
Crystal Structure of Human Type III Fibronectin Extradomain B and Domain 8 2gys 
2.7 A structure of the extracellular domains of the human beta common receptor involved in IL-3, IL-5, and GM-CSF signalling 2h41 
Solution structure of the second type III domain of human Fibronectin: minimized average structure 2h45 
Solution structure of the second type III domain of human Fibronectin: ensemble of 25 structures 2ha1 
Complex of the first and second type III domains of human Fibronectin in solution 2haz 
Crystal structure of the first fibronectin domain of human NCAM1 2ibb 
Crystal Structure of the First and Second FNIII Domains of Ihog 2ibg 
Crystal Structure of Hedgehog Bound to the FNIII Domains of Ihog 2ic2 
Crystal Structure of the First FNIII Domain of Ihog 2jix 
Crystal structure of ABT-007 FAB fragment with the soluble domain of EPO receptor 2jll 
Crystal structure of NCAM2 IgIV-FN3II 2kbg 
Solution structure of the second Fibronectin type-III module of NCAM2 2lfg 
Solution structure of the human prolactin receptor ecd domain d2 2m26 
NMR structure of the C-terminal domain of the protein HCFC1 from Mus musculus 2mfn 
SOLUTION NMR STRUCTURE OF LINKED CELL ATTACHMENT MODULES OF MOUSE FIBRONECTIN CONTAINING THE RGD AND SYNERGY REGIONS, 10 STRUCTURES 2mnu 
2MNU 2n1k 
2N1K 2nzi 
Crystal structure of domains A168-A170 from titin 2obg 
Crystal Structure of Monobody MBP-74/Maltose Binding Protein Fusion Complex 2ocf 
Human estrogen receptor alpha ligand-binding domain in complex with estradiol and the E2#23 FN3 monobody 2q7n 
Crystal structure of Leukemia inhibitory factor in complex with LIF receptor (domains 1-5) 2qbw 
The crystal structure of PDZ-Fibronectin fusion protein 2rb8 
High resolution design of a protein loop 2rbl 
High resolution design of a protein loop 2uve 
Structure of Yersinia enterocolitica Family 28 Exopolygalacturonase 2uvf 
Structure of Yersinia enterocolitica Family 28 Exopolygalacturonase in Complex with Digalaturonic Acid 2v5y 
Crystal structure of the receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase mu ectodomain 2vkw 
Human NCAM, FN3 domains 1 and 2 2vkx 
Human NCAM, FN3 domains 1 and 2, M610R mutant 2vtc 
The structure of a glycoside hydrolase family 61 member, Cel61B from the Hypocrea jecorina. 2w1n 
cohesin and fibronectin type-III double module construct from the Clostridium perfringens glycoside hydrolase GH84C 2x10 
Crystal structure of the complete EphA2 ectodomain 2x11 
Crystal structure of the complete EphA2 ectodomain in complex with ephrin A5 receptor binding domain 2xyc 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF NCAM2 IGIV-FN3I 2yrz 
Solution structure of the fibronectin type III domain of human Integrin beta-4 2yuw 
Solution Structure of 2nd Fibronectin Domain of Slow Type Myosin-Binding Protein C 2yux 
Solution Structure of 3rd Fibronectin type three Domain of slow type Myosin-Binding Protein C 3b83 
Computer-Based Redesign of a beta Sandwich Protein Suggests that Extensive Negative Design Is Not Required for De Novo beta Sheet Design. 3bpl 
Crystal structure of the IL4-IL4R-Common Gamma ternary complex 3bpn 
Crystal structure of the IL4-IL4R-IL13Ra ternary complex 3bpo 
Crystal structure of the IL13-IL4R-IL13Ra ternary complex 3ch8 
The crystal structure of PDZ-Fibronectin fusion protein 3csb 
Crystal Structure of Monobody YSX1/Maltose Binding Protein Fusion Complex 3csg 
Crystal Structure of Monobody YS1(MBP-74)/Maltose Binding Protein Fusion Complex 3d1m 
Crystal Structure of Sonic Hedgehog Bound to the third FNIII domain of CDO 3d48 
Crystal structure of a prolactin receptor antagonist bound to the extracellular domain of the prolactin receptor 3e0g 
Structure of the Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Receptor (LIF-R) domains D1-D5 3ew3 
the 1:2 complex between a Nterminal elongated prolactin and the extra cellular domain of the rat prolactin receptor 3f7p 
Crystal structure of a complex between integrin beta4 and plectin 3f7q 
First pair of Fibronectin type III domains and part of the connecting segment of the integrin beta4 3f7r 
First pair of Fibronectin type III domains and part of the connecting segment of the integrin beta4 3fl7 
Crystal structure of the human ephrin A2 ectodomain 3hhr 
HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE AND EXTRACELLULAR DOMAIN OF ITS RECEPTOR: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE COMPLEX 3k2m 
Crystal Structure of Monobody HA4/Abl1 SH2 Domain Complex 3l5h 
Crystal structure of the full ectodomain of human gp130: New insights into the molecular assembly of receptor complexes 3l5i 
Crystal structure of FnIII domains of human GP130 (Domains 4-6) 3l5j 
Crystal structure of FnIII domains of human GP130 (Domains 4-6) 3lpw 
Crystal structure of the FnIII-tandem A77-A78 from the A-band of titin 3lqm 
Structure of the IL-10R2 Common Chain 3mpc 
The crystal structure of a Fn3-like protein from Clostridium thermocellum 3mtr 
Crystal structure of the Ig5-FN1 tandem of human NCAM 3mx0 
Crystal Structure of EphA2 ectodomain in complex with ephrin-A5 3mzg 
Crystal structure of a human prolactin receptor antagonist in complex with the extracellular domain of the human prolactin receptor 3n06 
A mutant human Prolactin receptor antagonist H27A in complex with the extracellular domain of the human prolactin receptor 3n0p 
A mutant human Prolactin receptor antagonist H30A in complex with the extracellular domain of the human prolactin receptor 3n1f 
Crystal Structure of IhhN bound to CDOFn3 3n1g 
Crystal structure of DhhN bound to BOCFn3 3n1m 
Crystal Structure of IhhN bound to BOCFn3 3n1p 
Crystal Structure of IhhN bound to BOCFn3 3n1q 
Crystal Structure of DhhN bound to CDOFn3 3ncb 
A mutant human Prolactin receptor antagonist H180A in complex with the extracellular domain of the human prolactin receptor 3ncc 
A human Prolactin receptor antagonist in complex with the mutant extracellular domain H188A of the human prolactin receptor 3nce 
A mutant human Prolactin receptor antagonist H27A in complex with the mutant extracellular domain H188A of the human prolactin receptor 3ncf 
A mutant human Prolactin receptor antagonist H30A in complex with the mutant extracellular domain H188A of the human prolactin receptor 3npz 
Prolactin Receptor (PRLR) Complexed with the Natural Hormone (PRL) 3p4l 
Crystal structure of a hemojuvelin-binding fragment of neogenin 3qaz 
IL-2 mutant D10 ternary complex 3qb7 
Interleukin-4 mutant RGA bound to cytokine receptor common gamma 3qht 
Crystal Structure of the Monobody ySMB-1 bound to yeast SUMO 3qwq 
Crystal structure of the extracellular domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor in complex with an adnectin 3qwr 
Crystal structure of IL-23 in complex with an adnectin 3r4d 
Crystal structure of mouse coronavirus receptor-binding domain complexed with its murine receptor 3r8q 
Structure of Fibronectin domain 12-14 3rzw 
Crystal Structure of the Monobody ySMB-9 bound to human SUMO1 3s98 
human IFNAR1 3se3 
human IFNa2-IFNAR ternary complex 3se4 
human IFNw-IFNAR ternary complex 3t04 
Crystal structure of monobody 7c12/abl1 sh2 domain complex 3t1w 
Structure of the four-domain fragment Fn7B89 of oncofetal fibronectin 3tes 
Crystal Structure of Tencon 3teu 
Crystal structure of fibcon 3tgx 
IL-21:IL21R complex 3uto 
Twitchin kinase region from C.elegans (Fn31-NL-kin-CRD-Ig26) 3uyo 
Crystal structure of monobody SH13/ABL1 SH2 domain complex 3wcy 
Murine Ifnar1 in complex with interferon-beta 3wih 
3WIH 4bk4 
crystal structure of the human EphA4 ectodomain 4bk5 
crystal structure of the human EphA4 ectodomain in complex with human ephrin A5 (amine-methylated sample) 4bka 
crystal structure of the human EphA4 ectodomain in complex with human ephrin A5 4bkf 
crystal structure of the human EphA4 ectodomain in complex with human ephrinB3 4bq6 
Crystal structure of the RGMB-NEO1 complex form 1 4bq7 
Crystal structure of the RGMB-Neo1 complex form 2 4bq8 
Crystal structure of the RGMB-NEO1 complex form 3 4bq9 
Crystal structure of the FN5 and FN6 domains of NEO1, form 1 4bqb 
Crystal structure of the FN5 and FN6 domains of NEO1, form 2 4bqc 
Crystal structure of the FN5 and FN6 domains of NEO1 bound to SOS 4doh 
IL20/IL201/IL20R2 Ternary Complex 4gh7 
Crystal structure of Anticalin N7A in complex with oncofetal fibronectin fragment Fn7B8 4go6 
Crystal structure of HCF-1 self-association sequence 1 4gs7 
Structure of the Interleukin-15 quaternary complex 4hlj 
Axon Guidance Receptor 4huk 
MATE transporter NorM-NG in complex with TPP and monobody 4hul 
MATE transporter NorM-NG in complex with Cs+ and monobody 4hum 
MATE transporter NorM-NG in complex with ethidium and monobody 4hun 
MATE transporter NorM-NG in complex with R6G and monobody 4hwb 
Crystal structure of ectodomain 3 of the IL-13 receptor alpha 1 in complex with a human neutralizing monoclonal antibody fragment 4i18 
Crystal structure of human prolactin receptor complexed with Fab fragment 4je4 
Crystal Structure of Monobody NSa1/SHP2 N-SH2 Domain Complex 4jeg 
Crystal Structure of Monobody CS1/SHP2 C-SH2 Domain Complex 4jmg 
Crystal structure of the synthetic protein in complex with pY peptide 4jmh 
Crystal structure of synthetic protein in complex with double pY peptide 4k0v 
Structural basis for angiopoietin-1 mediated signaling initiation 4lpt 
Crystal structure of monomeric TENCON variant P54CR4-31 4lpu 
Crystal structure of TENCON variant P40AR2-32R2 4lpv 
Crystal structure of TENCON variant P41BR3-42 4lpw 
Crystal structure of TENCON variant A6 4lpx 
Crystal structure of TENCON variant D4 4lpy 
Crystal structure of TENCON variant G10 4lsd 
Myokine structure 4lxo 
4LXO 4m4p 
Crystal structure of EPHA4 ectodomain 4m4r 
Epha4 ectodomain complex with ephrin a5 4m6a 
N-Terminal beta-Strand Swapping in a Consensus Derived Alternative Scaffold Driven by Stabilizing Hydrophobic Interactions 4mmx 
Integrin AlphaVBeta3 ectodomain bound to the tenth domain of Fibronectin 4mmy 
Integrin AlphaVBeta3 ectodomain bound to the tenth domain of Fibronectin with the IAKGDWND motif 4mmz 
Integrin AlphaVBeta3 ectodomain bound to an antagonistic tenth domain of Fibronectin 4n5u 
Crystal structure of the 4th FN3 domain of human Protein Tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type F [PSI-NYSGRC-006240] 4n68 
Crystal structure of an internal FN3 domain from human Contactin-5 [PSI-NYSGRC-005804] 4nkq 
4NKQ 4nn5 
Cytokine receptor complex - Crystal form 1A 4nn6 
Cytokine receptor complex - Crystal form 1B 4nn7 
Cytokine receptor complex - Crystal form 2 4nzd 
4NZD 4o00 
4O00 4ov6 
4OV6 4pbx 
4PBX 4pln 
4PLN 4plo 
4PLO 4q58 
4Q58 4q66 
4Q66 4qqv 
4QQV 4rs1 
4RS1 4s0s 
4S0S 4s0t 
4S0T 4s3l 
4S3L 4u3h 
4U3H 4ui2 
4UI2 4urt 
4URT 4wtw 
4WTW 4wtx 
4WTX 4y5v 
4Y5V 4y5x 
4Y5X 4y5y 
4Y5Y 4y61 
4Y61 4yfd 
4YFD 4yfe 
4YFE 4yfg 
4YFG 4yg8 
4YG8 4yh7 
4YH7 4zxb 
4ZXB 5a40 
5A40 5a43 
5A43 5c6p 
5C6P 5dc0 
5DC0 5dc4 
5DC4 5dc9 
5DC9 5dft 
5DFT 5dwu 
5DWU 5e4e 
5E4E 5e4q 
5E4Q 5e4s 
5E4S 5e52 
5E52 5e53 
5E53 5e55 
5E55 5e7l 
5E7L 5e95 
5E95 5ecj 
5ECJ 5eh1 
5EH1 5fm4 
5FM4 5fm5 
5FM5 5fm8 
5FM8 5fmv 
5FMV 5fn6 
5FN6 5fn8 
5FN8 5fxb 
5FXB 5g56 
5G56 5hx2 
5HX2 5i99 
5I99 5iv5 
5IV5 5iv7 
5IV7 5j67 
5J67 5j68 
5J68 5j7c 
5J7C 5j7k 
5J7K 5kbn 
5KBN 5kf4 
5KF4 5kom 
5KOM 5kvm 
5KVM 5l2h 
5L2H 5lkn 
5LKN - Links (links to other resources describing this domain)
-
PROSITE FN3_DOMAIN INTERPRO IPR003961 PFAM fn3

