The domain within your query sequence starts at position 27 and ends at position 253; the E-value for the PH domain shown below is 3.23e-8.
PLRRRCSSCCFPGEYHLGRSRRKSVPGGKQYSMEAAPAAPFRPSQGFLSRRLKSSIKRTK SQPKLDRTSSFRQILPRFRSADHDRARLMQSFKESHSHESLLSPSSAAEALELNLDEDSI IKPVHSSILGQEFCFEVTTSSGTKCFACRSAAERDKWIENLQRAVKPNKDNSRRVDNVLK LWIIEARELPPKKRYYCELCLDDMLYARTTSKPRSASGDTVFWGEHF
PHPleckstrin homology domain. |
|---|
| SMART accession number: | SM00233 |
|---|---|
| Description: | Domain commonly found in eukaryotic signalling proteins. The domain family possesses multiple functions including the abilities to bind inositol phosphates, and various proteins. PH domains have been found to possess inserted domains (such as in PLC gamma, syntrophins) and to be inserted within other domains. Mutations in Brutons tyrosine kinase (Btk) within its PH domain cause X-linked agammaglobulinaemia (XLA) in patients. Point mutations cluster into the positively charged end of the molecule around the predicted binding site for phosphatidylinositol lipids. |
| Interpro abstract (IPR001849): | Pleckstrin homology (PH) domains are small modular domains that occur in a large variety of proteins. The domains can bind phosphatidylinositol within biological membranes and proteins such as the beta/gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins [ (PUBMED:8074669) ] and protein kinase C [ (PUBMED:7522330) ]. Through these interactions, PH domains play a role in recruiting proteins to different membranes, thus targeting them to appropriate cellular compartments or enabling them to interact with other components of the signal transduction pathways. PH domains have been found to possess inserted domains (such as in PLC gamma, syntrophins) and to be inserted within other domains. Mutations in Brutons tyrosine kinase (Btk) within its PH domain cause X-linked agammaglobulinaemia (XLA) in patients. Point mutations cluster into the positively charged end of the molecule around the predicted binding site for phosphatidylinositol lipids. The 3D structure of several PH domains has been determined [ (PUBMED:7634082) ]. All known cases have a common structure consisting of two perpendicular anti-parallel beta sheets, followed by a C-terminal amphipathic helix. The loops connecting the beta-strands differ greatly in length, making the PH domain relatively difficult to detect. There are no totally invariant residues within the PH domain. Proteins reported to contain one more PH domains belong to the following families:
|
| Family alignment: |
There are 196127 PH domains in 171590 proteins in SMART's nrdb database.
Click on the following links for more information.
- Evolution (species in which this domain is found)
-
Taxonomic distribution of proteins containing PH domain.
This tree includes only several representative species. The complete taxonomic breakdown of all proteins with PH domain is also avaliable.
Click on the protein counts, or double click on taxonomic names to display all proteins containing PH domain in the selected taxonomic class.
- Cellular role (predicted cellular role)
-
Cellular role: signalling
Binding / catalysis: inositol 1, 3, 4, 5-tetrakisphosphate-binding, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate-binding - Literature (relevant references for this domain)
-
Primary literature is listed below; Automatically-derived, secondary literature is also avaliable.
- Lemmon MA, Ferguson KM
- Pleckstrin homology domains.
- Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1998; 228: 39-74
- Carugo KD, Banuelos S, Saraste M
- Crystal structure of a calponin homology domain.
- Nat Struct Biol. 1997; 4: 175-9
- Display abstract
The three-dimensional structure of the calponin homology domain present in many actin binding cytoskeletal and signal-transducing proteins has been determined at 2.0 A resolution.
- Fukuda M, Mikoshiba K
- The function of inositol high polyphosphate binding proteins.
- Bioessays. 1997; 19: 593-603
- Display abstract
The inositol phosphate metabolism network has been found to be much more complex than previously thought, as more and more inositol phosphates and their metabolizing enzymes have been discovered. Some of the inositol phosphates have been shown to have biological activities, but little is known about their signal transduction mechanisms except for that of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. The recent discovery, however, of a number of binding proteins for inositol high polyphosphate [inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate (IP4), inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate, or inositol hexakisphosphate] enables us to speculate on the physiological function of these compounds. In this article we focus on two major issues: (1) the roles of inositol high polyphosphates in vesicular trafficking, especially exocytosis, and (2) pleckstrin homology domain-containing IP4 binding proteins involved in the Ras signaling pathway.
- Hyvonen M, Saraste M
- Structure of the PH domain and Btk motif from Bruton's tyrosine kinase: molecular explanations for X-linked agammaglobulinaemia.
- EMBO J. 1997; 16: 3396-404
- Display abstract
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) is an enzyme which is involved in maturation of B cells. It is a target for mutations causing X-linked agammaglobulinaemia (XLA) in man. We have determined the structure of the N-terminal part of Btk by X-ray crystallography at 1.6 A resolution. This part of the kinase contains a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain and a Btk motif. The structure of the PH domain is similar to those published previously: a seven-stranded bent beta-sheet with a C-terminal alpha-helix. Individual point mutations within the Btk PH domain which cause XLA can be classified as either structural or functional in the light of the three-dimensional structure and biochemical data. All functional mutations cluster into the positively charged end of the molecule around the predicted binding site for phosphatidylinositol lipids. It is likely that these mutations inactivate the Btk pathway in cell signalling by reducing its affinity for inositol phosphates, which causes a failure in translocation of the kinase to the cell membrane. A small number of signalling proteins contain a Btk motif that always follows a PH domain in the sequence. This small module has a novel fold which is held together by a zinc ion bound by three conserved cysteines and a histidine. The Btk motif packs against the second half of the beta-sheet of the PH domain, forming a close contact with it. Our structure opens up new ways to study the role of the PH domain and Btk motif in the cellular function of Btk and the molecular basis of its dysfunction in XLA patients.
- Muhlberg AB, Warnock DE, Schmid SL
- Domain structure and intramolecular regulation of dynamin GTPase.
- EMBO J. 1997; 16: 6676-83
- Display abstract
Dynamin is a 100 kDa GTPase required for receptor-mediated endocytosis, functioning as the key regulator of the late stages of clathrin-coated vesicle budding. It is specifically targeted to clathrin-coated pits where it self-assembles into 'collars' required for detachment of coated vesicles from the plasma membrane. Self-assembly stimulates dynamin GTPase activity. Thus, dynamin-dynamin interactions are critical in regulating its cellular function. We show by crosslinking and analytical ultracentrifugation that dynamin is a tetramer. Using limited proteolysis, we have defined structural domains of dynamin and evaluated the domain interactions and requirements for self-assembly and GTP binding and hydrolysis. We show that dynamin's C-terminal proline- and arginine-rich domain (PRD) and dynamin's pleckstrin homology (PH) domain are, respectively, positive and negative regulators of self-assembly and GTP hydrolysis. Importantly, we have discovered that the alpha-helical domain interposed between the PH domain and the PRD interacts with the N-terminal GTPase domain to stimulate GTP hydrolysis. We term this region the GTPase effector domain (GED) of dynamin.
- Tanaka K et al.
- A target of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate with a zinc finger motif similar to that of the ADP-ribosylation-factor GTPase-activating protein and two pleckstrin homology domains.
- Eur J Biochem. 1997; 245: 512-9
- Display abstract
We have purified a protein that binds phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate [PtdIns(3,4,5)P3] using beads bearing a PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 analogue. This protein, with a molecular mass of 43 kDa, was termed PtdIns(3,4,5)P3-binding protein. The partial amino acid sequences were determined and a full-length cDNA encoding the protein was isolated from bovine brain cDNA library. The clone harbored an open reading frame of 373 amino acids which contained one zinc finger motif similar to that of ADP-ribosylation-factor GTPase-activating protein and two pleckstrin homology domains. The entire sequence was 83% similar to centaurin alpha, another PtdIns(3,4,5)P3-binding protein. The protein bound PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 with a higher affinity than it did inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate, and phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate suggesting that the binding to PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 was specific. The binding activity was weaker in the mutants with a point mutation in the conserved sequences in each pleckstrin homology domain. Introduction of both mutations abolished the activity. These results suggest that this new binding protein binds PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 through two pleckstrin domains present in the molecule.
- Perez-Alvarado GC, Kosa JL, Louis HA, Beckerle MC, Winge DR, Summers MF
- Structure of the cysteine-rich intestinal protein, CRIP.
- J Mol Biol. 1996; 257: 153-74
- Display abstract
LIM domains are Zn-binding arrays found in a number of proteins involved in the control of cell differentiation, including several developmentally regulated transcription factors and a human proto-oncogene product. The rat cysteine-rich intestinal protein, CRIP, is a 76-residue polypeptide which contains a LIM motif. The solution structure of CRIP has been determined by homonuclear and 1H-15N heteronuclear correlated nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Structures with individual distance violations of < or = 0.03 angstrom and penalties (squared sum of distance violations) of < or = 0.06 angstrom2 were generated with a total of 500 nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE)-derived distance restraints (averaging 15.6 restraints per refined residue). Superposition of backbone heavy atoms of ordered residues relative to mean atom positions is achieved with pairwise rms deviations of 0.54(+/-0.14) angstrom. As observed previously for a peptide with the sequence of the C-terminal LIM domain from the avian cysteine-rich protein, CRP (cCRP-LIM2), CRIP binds two equivalents of zinc, forming N-terminal CCHC (Cys3, Cys6, His24, Cys27) and C-terminal CCCC (Cys30, Cys33, Cys51, Cys55) modules. The CCHC and CCCC modules in CRIP contain two orthogonally-arrayed antiparallel beta-sheets. The C-terminal end of the CCHC module contains a tight turn and the C terminus of the CCCC module forms an alpha-helix. The modules pack via hydrophobic interactions, forming a compact structure that is similar to that observed for cCRP-LIM2. The most significant differences between the structures occur at the CCHC module-CCCC module interface, which results in a difference in the relative orientations of the modules, and at the C terminus where the alpha-helix appears to be packed more tightly against the preceding antiparallel beta-sheet. The greater abundance of NOE information obtained for CRIP relative to cCRP-LIM2, combined with the analysis of J-coupling and proton chemical shift data, have allowed a more detailed evaluation of the molecular level interactions that stabilize the fold of the LIM motif.
- Ponting CP, Bork P
- Pleckstrin's repeat performance: a novel domain in G-protein signaling?
- Trends Biochem Sci. 1996; 21: 245-6
- Sakane F, Imai S, Kai M, Wada I, Kanoh H
- Molecular cloning of a novel diacylglycerol kinase isozyme with a pleckstrin homology domain and a C-terminal tail similar to those of the EPH family of protein-tyrosine kinases.
- J Biol Chem. 1996; 271: 8394-401
- Display abstract
A fourth member of the diacylglycerol kinase (DGK) gene family termed DGK delta was cloned from the human testis cDNA library. The cDNA sequence contains an open reading frame of 3,507 nucleotides encoding a putative DGK protein of 130,006 Da. Interestingly, the new DGK isozyme contains a pleckstrin homology domain found in a number of proteins involved in signal transduction. Furthermore, the C-terminal tail of this isozyme is very similar to those of the EPH family of receptor tyrosine kinases. The primary structure of the delta-isozyme also has two cysteine-rich zinc finger-like structures (C3 region) and the C-terminal C4 region, both of which have been commonly found in the three isozymes previously cloned (DGKs alpha, beta and gamma). However, DGK delta lacks the EF-hand motifs (C2) and contains a long Glu- and Ser-rich insertion (317 residues), which divides the C4 region into two portions. Taken together, these structural features of DGK delta indicate that this isozyme belongs to a DGK subfamily distinct from that consisting of DGKs alpha, beta, and gamma. Increased DGK activity without marked preference to arachidonoyl type of diacylglycerol was detected in the particulate fraction of COS-7 cells expressing the transfected DGKdelta cDNA. The enzyme activity was independent of phosphatidylserine, which is a common activator for the previously sequenced DGKs. Northern blot analysis showed that the DGK delta mRNA (approximately 6.3 kilobases) is most abundant in human skeletal muscle but undetectable in the brain, thymus, and retina. This expression pattern is different from those of the previously cloned DGKs. Our results show that the DGK gene family consists of at least two subfamilies consisting of enzymes with distinct structural characteristics and that each cell type probably expresses its own characteristic repertoire of DGKs whose functions may be regulated through different signal transduction pathways.
- Shaw G
- The pleckstrin homology domain: an intriguing multifunctional protein module.
- Bioessays. 1996; 18: 35-46
- Display abstract
Pleckstrin homology (PH) domains are a family of compact protein modules defined by sequences of roughly 100 amino acids. These domains are common in vertebrate, Drosophila, C. elegans and yeast proteins, suggesting an early origin and fundamental importance to eukaryotic biology. Many enzymes which have important regulatory functions contain PH domains, and mutant forms of several such proteins are implicated in oncogenesis and developmental disorders. Numerous recent studies show that PH domains bind various proteins and inositolphosphates. Here I discuss PH domains in detail and conclude that they form a versatile family of membrane binding and protein localization modules.
- Thornton KH, Mueller WT, McConnell P, Zhu G, Saltiel AR, Thanabal V
- Nuclear magnetic resonance solution structure of the growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 Src homology 2 domain.
- Biochemistry. 1996; 35: 11852-64
- Display abstract
A family of NMR solution structures of the growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (Grb2) SH2 domain has been determined by heteronuclear multidimensional NMR. Proton, nitrogen, and carbon chemical shift assignments have been made for the SH2 domain of Grb2. Assignments were made from a combination of homonuclear two-dimensional and 15N- and 13C-edited three-dimensional spectra at pH 6.2 and 298 K. Structure-induced proton and carbon secondary shifts were calculated and used to facilitate the spectral assignment process. NOE, scalar coupling, secondary chemical shift, and amide proton exchange data were used to characterize the secondary structural elements and hydrogen-bonding network in the Grb2 SH2 domain. The three-dimensional structure of the Grb2 SH2 domain was calculated using 1112 restraints obtained from NOE, coupling constant, and amide proton exchange data. The rmsd for the 24 calculated structures to the mean structure of the Grb2 SH2 domain was 0.75 A for backbone and 1.28 A for all heavy atoms. The three-dimensional fold of the Grb2 SH2 domain is similar to that observed for other SH2 domains and consists of two alpha-helical segments and eight beta-strands, six strands that make up two contiguous antiparallel beta-sheets, and two strands that form two short parallel beta-sheets. The structure of the phosphotyrosine binding pocket of Grb2 is similar to that observed for other SH2 domains. The hydrophobic binding pocket of Grb2 is similar to that observed for Src with the exception that tryptophan 121 of Grb2 occupies part of the pY+3 binding pocket. Structural implications for the Grb2 SH2 domain selectivity at the pY+2 and pY+3 sites are discussed.
- Ferguson KM, Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J, Sigler PB
- Structure of the high affinity complex of inositol trisphosphate with a phospholipase C pleckstrin homology domain.
- Cell. 1995; 83: 1037-46
- Display abstract
The X-ray crystal structure of the high affinity complex between the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain from rat phospholipase C-delta 1 (PLC-delta 1) and inositol-(1,4,5)-trisphosphate (Ins(1,4,5)P3) has been refined to 1.9 A resolution. The domain fold is similar to others of known structure. Ins(1,4,5)P3 binds on the positively charged face of the electrostatically polarized domain, interacting predominantly with the beta 1/beta 2 and beta 3/beta 4 loops. The 4- and 5-phosphate groups of Ins(1,4,5)P3 interact much more extensively than the 1-phosphate. Two amino acids in the PLC-delta 1 PH domain that contact Ins(1,4,5)P3 have counterparts in the Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) PH domain, where mutational changes cause inherited agammaglobulinemia, suggesting a mechanism for loss of function in Btk mutants. Using electrostatics and varying levels of head-group specificity, PH domains may localize and orient signaling proteins, providing a general membrane targeting and regulatory function.
- Fushman D, Cahill S, Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J, Cowburn D
- Solution structure of pleckstrin homology domain of dynamin by heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy.
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995; 92: 816-20
- Display abstract
The pleckstrin homology (PH) domain is a recognition motif thought to be involved in signal-transduction pathways controlled by a variety of cytoplasmic proteins. Assignments of nearly all 1H, 13C, and 15N resonances of the PH domain from dynamin have been obtained from homonuclear and heteronuclear NMR experiments. The secondary structure has been elucidated from the pattern of nuclear Overhauser enhancements, from 13C chemical shift deviations, and from observation of slowly exchanging amide hydrogens. The secondary structure contains one alpha-helix and eight beta-strands, seven of which are arranged in two contiguous, antiparallel beta-sheets. The structure is monomeric, in contrast to the well-defined intimate dimerization of the crystal structure of this molecule. Residues possibly involved in ligand binding are in apparently flexible loops. Steady-state 15N(1H) nuclear Overhauser effect measurements indicate unequivocally the boundaries of this PH domain, and the structured portion of the domain appears to be more extended to the C terminus than previously suggested for other PH domains.
- Hyvonen M, Macias MJ, Nilges M, Oschkinat H, Saraste M, Wilmanns M
- Structure of the binding site for inositol phosphates in a PH domain.
- EMBO J. 1995; 14: 4676-85
- Display abstract
Phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate has been found to bind specifically to pleckstrin homology (PH) domains that are commonly present in signalling proteins but also found in cytoskeleton. We have studied the complexes of the beta-spectrin PH domain and soluble inositol phosphates using both circular dichroism and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and X-ray crystallography. The specific binding site is located in the centre of a positively charged surface patch of the domain. The presence of 4,5-bisphosphate group on the inositol ring is critical for binding. In the crystal structure that has been determined at 2.0 A resolution, inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate is bound with salt bridges and hydrogen bonds through these phosphate groups whereas the 1-phosphate group is mostly solvent-exposed and the inositol ring has virtually no interactions with the protein. We propose a model in which PH domains are involved in reversible anchoring of proteins to membranes via their specific binding to phosphoinositides. They could also participate in a response to a second messenger such as inositol trisphosphate, organizing cross-roads in cellular signalling.
- Ponting CP
- SAM: a novel motif in yeast sterile and Drosophila polyhomeotic proteins.
- Protein Sci. 1995; 4: 1928-30
- Display abstract
Single copies of an approximately 65-70 residue domain are shown to be present in the sequences of 14 eukaryotic proteins, including yeast byr2, STE11, ste4, and STE50, which are essential participants in sexual differentiation. This domain, named SAM (sterile alpha motif), appears to participate in other developmental processes because it is also present in Drosophila polyhomeotic gene product and related homologues, which are thought to regulate determination of segmental specification in early embryogenesis. Its appearance in byr2 and STE11, which are MEK kinases, and in proteins containing pleckstrain homology, src homology 3, and discs-large homologous region domains, suggests possible participation in signal transduction pathways.
- Xiao B et al.
- Structure of a 14-3-3 protein and implications for coordination of multiple signalling pathways.
- Nature. 1995; 376: 188-91
- Display abstract
A broad range of organisms and tissues contain 14-3-3 proteins, which have been associated with many diverse functions including critical roles in signal transduction pathways, exocytosis and cell cycle regulation. We report here the crystal structure of the human T-cell 14-3-3 isoform (tau) dimer at 2.6 A resolution. Each monomer (Mr 28K) is composed of an unusual arrangement of nine antiparallel alpha-helices organized as two structural domains. The dimer creates a large, negatively charged channel approximately 35 A broad, 35 A wide and 20 A deep. Overall, invariant residues line the interior of this channel whereas the more variable residues are distributed on the outer surface. At the base of this channel is a 16-residue segment of 14-3-3 which has been implicated in the binding of 14-3-3 to protein kinase C.
- Zhang P, Talluri S, Deng H, Branton D, Wagner G
- Solution structure of the pleckstrin homology domain of Drosophila beta-spectrin.
- Structure. 1995; 3: 1185-95
- Display abstract
BACKGROUND: The pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, which is approximately 100 amino acids long, has been found in about 70 proteins involved in signal transduction and cytoskeletal function, a frequency comparable to SH2 (src homology 2) and SH3 domains. PH domains have been shown to bind the beta gamma-subunits of G-proteins and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2). It is conceivable that the PH domain of beta-spectrin plays a part in the association of spectrin with the plasma membrane of cells. RESULTS: We have solved the solution structure of the 122-residue PH domain of Drosophila beta-spectrin. The overall fold consists of two antiparallel beta-sheets packing against each other at an angle of approximately 60 degrees to form a beta-sandwich, a two-turn alpha-helix unique to spectrin PH domains, and a four-turn C-terminal alpha-helix. One of the major insertions in beta-spectrin PH domains forms a long, basic surface loop and appears to undergo slow conformational exchange in solution. This loop shows big spectral changes upon addition of D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3). CONCLUSIONS: We propose that the groove at the outer surface of the second beta-sheet is an important site of association with other proteins. This site and the possible lipid-binding site can serve to localize the spectrin network under the plasma membrane. More generally, it has to be considered that the common fold observed for the PH domain structures solved so far does not necessarily mean that all PH domains have similar functions. In fact, the residues constituting potential binding sites for ligands or other proteins are only slightly conserved between different PH domains.
- Zhou MM et al.
- Structure and ligand recognition of the phosphotyrosine binding domain of Shc.
- Nature. 1995; 378: 584-92
- Display abstract
The nuclear magnetic resonance structure of the phosphotyrosine binding (PTB) domain of Shc complexed to a phosphopeptide reveals an alternative means of recognizing tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins. Unlike in SH2 domains, the phosphopeptide forms an antiparallel beta-strand with a beta-sheet of the protein, interacts with a hydrophobic pocket through the (pY-5) residue, and adopts a beta-turn. The PTB domain is structurally similar to pleckstrin homology domains (a beta-sandwich capped by an alpha-helix) and binds to acidic phospholipids, suggesting a possible role in membrane localization.
- Downing AK, Driscoll PC, Gout I, Salim K, Zvelebil MJ, Waterfield MD
- Three-dimensional solution structure of the pleckstrin homology domain from dynamin.
- Curr Biol. 1994; 4: 884-91
- Display abstract
BACKGROUND: The pleckstrin homology (PH) domain is a region of approximately 100 amino acids, defined by sequence similarity, that has been found in about 60 proteins, many of which are involved in signal transduction downstream of cell surface receptors; the function of PH domains is unknown. The only clue to the function of PH domains is the circumstantial evidence that they may link beta gamma subunits of G proteins to second messenger systems. Knowledge of the three-dimensional structures of PH domains should help to elucidate the roles they play in the proteins that contain them. RESULTS: Using homonuclear and heteronuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, we have determined the solution structure of the PH domain of the GTPase dynamin, one of a number of proteins that have PH domains and interact with GTP. The fold of the dynamin PH domain is composed of two antiparallel beta-sheets, which pack face-to-face at an angle of approximately 60 degrees. The first beta-sheet comprises four strands (residues 13-58) from the amino-terminal half of the protein sequence; the second beta-sheet contains three strands (residues 63-99). A single alpha-helix (residues 102-116) flanks one edge of the interface between the two sheets, parallel in orientation to the second sheet, in an alpha/beta roll motif similar to that of the B oligomer of verotoxin-1 from Escherichia coli. CONCLUSIONS: The structure of the dynamin PH domain is very similar to the recently reported structures of the pleckstrin and spectrin PH domains. This shows that, despite the low level of sequence similarity between different PH domains, they do have a characteristic polypeptide fold. On the basis of our structure, the suggestion that PH domains engage in coiled-coil interactions with G protein beta gamma subunits seems unlikely and should be re-evaluated.
- Ferguson KM, Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J, Sigler PB
- Crystal structure at 2.2 A resolution of the pleckstrin homology domain from human dynamin.
- Cell. 1994; 79: 199-209
- Display abstract
The X-ray crystal structure of the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain from human dynamin has been refined to 2.2 A resolution. A seven-stranded beta sandwich of two orthogonal antiparallel beta sheets is closed at one corner by a C-terminal alpha helix. Opposite this helix are the three loops that vary most among PH domains. The basic fold is very similar to that of two other PH domains recently determined by nuclear magnetic resonance, confirming that PH domain with known structure is electrostatically polarized, with the three variable loops forming a positively charged surface. This surface includes the position of the X-linked immunodeficiency mutation in the Btk PH domain and may serve as a ligand-binding surface.
- Gibson TJ, Hyvonen M, Musacchio A, Saraste M, Birney E
- PH domain: the first anniversary.
- Trends Biochem Sci. 1994; 19: 349-53
- Harlan JE, Hajduk PJ, Yoon HS, Fesik SW
- Pleckstrin homology domains bind to phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate.
- Nature. 1994; 371: 168-70
- Display abstract
The pleckstrin homology (PH) domain is a new protein module of around 100 amino acids found in several proteins involved in signal transduction. Although its specific function has yet to be elucidated, the carboxy-terminal regions of many PH domains bind to the beta gamma subunits of G proteins. On the basis of structural similarities between PH domains and lipid-binding proteins, we have proposed that PH domains may be binding to lipophilic molecules. Indeed, many of the proteins that contain this domain associate with phospholipid membranes, and disruption of this domain can interfere with membrane association. Here we report that PH domains bind to phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate and show that the lipid-binding site is located at the lip of the beta-barrel. This suggests that PH domains may be important for membrane localization of proteins through interactions with phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate.
- Macias MJ, Musacchio A, Ponstingl H, Nilges M, Saraste M, Oschkinat H
- Structure of the pleckstrin homology domain from beta-spectrin.
- Nature. 1994; 369: 675-7
- Display abstract
The 'pleckstrin homology' or PH domain is a 100-residue protein module. It is present in many kinases, different isoforms of phospholipase C, GTPase-activating proteins and nucleotide-exchange factors. Its function is not known, but many proteins that contain a PH domain interact with GTP-binding proteins. The PH domain in beta-adrenergic receptor kinase may be involved in binding to the beta gamma subunits of a trimeric G-protein. We report here the three-dimensional structure of the PH domain of the cytoskeletal protein spectrin using homonuclear nuclear magnetic resonance. The core of the molecule is an antiparallel beta-sheet consisting of seven strands. The C terminus is folded into a long alpha-helix, and another helix is present in one of the surface loops. The molecule is electrostatically polarized and contains a pocket which may be involved in the binding of a ligand. There is a distant relationship to the peptidyl-prolyl-cis-trans-isomerase FKBP in which this pocket is involved in the binding of the macrocyclic compound FK506 (refs 8-11).
- Timm D, Salim K, Gout I, Guruprasad L, Waterfield M, Blundell T
- Crystal structure of the pleckstrin homology domain from dynamin.
- Nat Struct Biol. 1994; 1: 782-8
- Display abstract
The pleckstrin homology (PH) domain is a conserved module present in many signal transducing and cytoskeletal proteins. Here we report the 2.8 A crystal structure of the PH domain from dynamin. This domain consists of seven beta-strands forming two roughly orthogonal antiparallel beta-sheets terminating with an amphipathic alpha-helix. The structure also reveals a non-covalent dimeric association of the PH domain and a hydrophobic pocket surrounded by a charged rim. The dynamin PH domain structure is discussed in relation to its potential role in mediating interactions between proteins.
- Vihinen M, Nilsson L, Smith CI
- Tec homology (TH) adjacent to the PH domain.
- FEBS Lett. 1994; 350: 263-5
- Display abstract
The pleckstrin homology (PH) domain is extended in the Btk kinase family by a region designated the TH (Tec homology) domain, which consists of about 80 residues preceding the SH3 domain. The TH domain contains a conserved 27 amino acid stretch designated the Btk motif and a proline-rich region. Sequence similarity was found to a putative Ras GTPase activating protein and a human interferon-gamma binding protein both in the PH domain and the Btk motif region. SLK1/SSP31 protein kinase and a non-catalytic p85 subunit of PI-3 kinase had similarity only with the proline rich region. The identification of a PH domain extension in some signal transduction proteins in different species suggests that this region is involved in protein-protein interactions.
- Yoon HS, Hajduk PJ, Petros AM, Olejniczak ET, Meadows RP, Fesik SW
- Solution structure of a pleckstrin-homology domain.
- Nature. 1994; 369: 672-5
- Display abstract
Pleckstrin, the major protein kinase C substrate of platelets, contains domains of about 100 amino acids at the amino and carboxy termini that have been found in a number of proteins, including serine/threonine kinases, GTPase-activating proteins, phospholipases and cytoskeletal proteins. These conserved sequences, termed pleckstrin-homology (PH) domains, are thought to be involved in signal transduction. But the details of the function and binding partners of the PH domains have not been characterized. Here we report the solution structure of the N-terminal pleckstrin-homology domain of pleckstrin determined using heteronuclear three-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The structure consists of an up-and-down beta-barrel of seven antiparallel beta-strands and a C-terminal amphiphilic alpha-helix that caps one end of the barrel. The overall topology of the domain is similar to that of the retinol-binding protein family of structures.
- Haslam RJ, Koide HB, Hemmings BA
- Pleckstrin domain homology.
- Nature. 1993; 363: 309-10
- Kohda D et al.
- Solution structure of the SH3 domain of phospholipase C-gamma.
- Cell. 1993; 72: 953-60
- Display abstract
SH3 (Src homology 3) domains are found in many signaling proteins and appear to function as binding modules for cytoplasmic target proteins. The solution structure of the SH3 domain of human phospholipase C-gamma (PLC-gamma) was determined by two-dimensional 1H NMR analysis. This SH3 domain is composed of eight antiparallel beta strands consisting of two successive "Greek key" motifs, which form a barrel-like structure. The conserved aliphatic and aromatic residues form a hydrophobic pocket on the molecular surface, and the conserved carboxylic residues are localized to the periphery. The hydrophobic pocket may serve as a binding site for target proteins. Analysis of the slowly exchanging amide protons by NMR measurements indicates that despite containing a high content of beta structure, the SH3 domain of PLC-gamma is flexible.
- Mayer BJ, Ren R, Clark KL, Baltimore D
- A putative modular domain present in diverse signaling proteins.
- Cell. 1993; 73: 629-30
- Musacchio A, Gibson T, Rice P, Thompson J, Saraste M
- The PH domain: a common piece in the structural patchwork of signalling proteins.
- Trends Biochem Sci. 1993; 18: 343-8
- Display abstract
The 'pleckstrin homology' domain is an approximately 100-residue protein module that has recently been added to the domain catalogue of signalling proteins. For this review we have made an extensive database search using a profile search method, and found a number of additional proteins that may contain PH domains. The PH domain is present in many kinases, isoforms of phospholipase C, GTPases, GTPase-activating proteins and nucleotide-exchange factors, including such proteins as Vav, Dbl and Bcr, and there are two PH domains in a guanine-nucleotide releasing factor of Ras. Many PH-domain-containing proteins interact with GTP-binding proteins. We have also identified a PH domain in beta-adrenergic receptor kinase exactly in the region that has already been shown to be involved in binding to the beta and gamma subunits of a heterotrimeric G protein. This suggests that PH domains may be involved in interactions with GTP-binding proteins.
- Musacchio A, Noble M, Pauptit R, Wierenga R, Saraste M
- Crystal structure of a Src-homology 3 (SH3) domain.
- Nature. 1992; 359: 851-5
- Display abstract
The Src-homologous SH3 domain is a small domain present in a large number of proteins that are involved in signal transduction, such as the Src protein tyrosine kinase, or in membrane-cytoskeleton interactions, but the function of SH3 is still unknown (reviewed in refs 1-3). Here we report the three-dimensional structure at 1.8 A resolution of the SH3 domain of the cytoskeletal protein spectrin expressed in Escherichia coli. The domain is a compact beta-barrel made of five antiparallel beta-strands. The amino acids that are conserved in the SH3 sequences are located close to each other on one side of the molecule. This surface is rich in aromatic and carboxylic amino acids, and is distal to the region of the molecule where the N and C termini reside and where SH3 inserts into the alpha-spectrin chain. We suggest that a protein ligand binds to this conserved surface of SH3.
- Disease (disease genes where sequence variants are found in this domain)
-
SwissProt sequences and OMIM curated human diseases associated with missense mutations within the PH domain.
Protein Disease Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK (Q06187) (SMART) OMIM:300300: Agammaglobulinemia, type 1, X-linked ; ?XLA and isolated growth hormone deficiency
OMIM:307200: - Metabolism (metabolic pathways involving proteins which contain this domain)
-
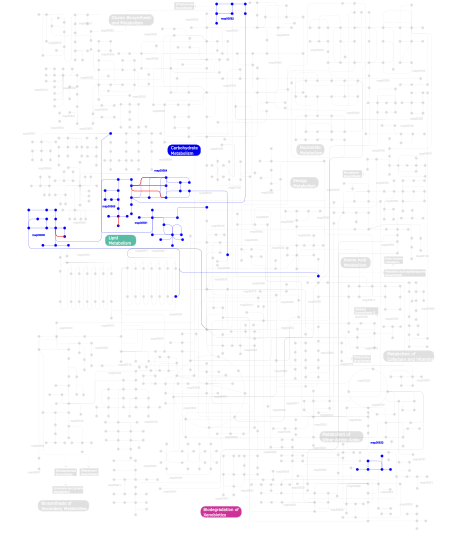
Click the image to view the interactive version of the map in iPath% proteins involved KEGG pathway ID Description 6.15 map04810 Regulation of actin cytoskeleton 4.81 map04664 Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway 4.70 map04510 Focal adhesion 4.14 map04660 T cell receptor signaling pathway 3.69 map04010 MAPK signaling pathway 3.69 map04012 ErbB signaling pathway 3.58 map04910 Insulin signaling pathway 3.24 map05223 Non-small cell lung cancer 3.13 map04670 Leukocyte transendothelial migration 3.13 map04650 Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity 3.07 map05214 Glioma 2.96 map05220 Chronic myeloid leukemia 2.85 map05211 Renal cell carcinoma 2.68 map04662 B cell receptor signaling pathway 2.52 map05210 Colorectal cancer 2.40 map05213 Endometrial cancer 2.40 map04070 Phosphatidylinositol signaling system 2.40 map05215 Prostate cancer 2.24 map04630 Jak-STAT signaling pathway 2.24 map04360 Axon guidance 2.24 map05221 Acute myeloid leukemia 2.18 map04370 VEGF signaling pathway 2.12 map04920 Adipocytokine signaling pathway 2.07  map00562
map00562Inositol phosphate metabolism 2.01 map05212 Pancreatic cancer 1.96 map04912 GnRH signaling pathway 1.90 map04020 Calcium signaling pathway 1.51 map04150 mTOR signaling pathway 1.45  map00564
map00564Glycerophospholipid metabolism 1.34 map05222 Small cell lung cancer 1.34 map04530 Tight junction 1.34 map04620 Toll-like receptor signaling pathway 1.34 map04210 Apoptosis 1.34 map05218 Melanoma 1.34 map04914 Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation 1.06  map00565
map00565Ether lipid metabolism 0.95 map05120 Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection 0.89 map04310 Wnt signaling pathway 0.89 map04350 TGF-beta signaling pathway 0.89 map04320 Dorso-ventral axis formation 0.89 map04540 Gap junction 0.78 map04930 Type II diabetes mellitus 0.67 map05040 Huntington's disease 0.39  map00561
map00561Glycerolipid metabolism 0.34 map04520 Adherens junction 0.34 map05030 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) 0.17 map03320 PPAR signaling pathway 0.11  map00600
map00600Sphingolipid metabolism 0.06  map00632
map00632Benzoate degradation via CoA ligation 0.06 map04610 Complement and coagulation cascades This information is based on mapping of SMART genomic protein database to KEGG orthologous groups. Percentage points are related to the number of proteins with PH domain which could be assigned to a KEGG orthologous group, and not all proteins containing PH domain. Please note that proteins can be included in multiple pathways, ie. the numbers above will not always add up to 100%.
- Structure (3D structures containing this domain)
3D Structures of PH domains in PDB
PDB code Main view Title 1awe 
HUMAN SOS1 PLECKSTRIN HOMOLOGY (PH) DOMAIN, NMR, 20 STRUCTURES 1b55 
PH DOMAIN FROM BRUTON'S TYROSINE KINASE IN COMPLEX WITH INOSITOL 1,3,4,5-TETRAKISPHOSPHATE 1bak 
SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PLECKSTRIN HOMOLOGY DOMAIN OF G-PROTEIN COUPLED RECEPTOR KINASE 2 (BETA-ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR KINASE 1), C-TERMINAL EXTENDED, NMR, 20 STRUCTURES 1btk 
PH DOMAIN AND BTK MOTIF FROM BRUTON'S TYROSINE KINASE MUTANT R28C 1btn 
STRUCTURE OF THE BINDING SITE FOR INOSITOL PHOSPHATES IN A PH DOMAIN 1bwn 
PH DOMAIN AND BTK MOTIF FROM BRUTON'S TYROSINE KINASE MUTANT E41K IN COMPLEX WITH INS(1,3,4,5)P4 1dbh 
DBL AND PLECKSTRIN HOMOLOGY DOMAINS FROM HSOS1 1dro 
NMR STRUCTURE OF THE CYTOSKELETON/SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PROTEIN 1dyn 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE AT 2.2 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION OF THE PLECKSTRIN HOMOLOGY DOMAIN FROM HUMAN DYNAMIN 1eaz 
Crystal structure of the phosphoinositol (3,4)-bisphosphate binding PH domain of TAPP1 from human. 1fao 
STRUCTURE OF THE PLECKSTRIN HOMOLOGY DOMAIN FROM DAPP1/PHISH IN COMPLEX WITH INOSITOL 1,3,4,5-TETRAKISPHOSPHATE 1fb8 
STRUCTURE OF THE PLECKSTRIN HOMOLOGY DOMAIN FROM DAPP1/PHISH 1fgy 
GRP1 PH DOMAIN WITH INS(1,3,4,5)P4 1fgz 
GRP1 PH DOMAIN (UNLIGANDED) 1fho 
Solution Structure of the PH Domain from the C. Elegans Muscle Protein UNC-89 1fhw 
Structure of the pleckstrin homology domain from GRP1 in complex with inositol(1,3,4,5,6)pentakisphosphate 1fhx 
Structure of the pleckstrin homology domain from GRP1 in complex with inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate 1foe 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF RAC1 IN COMPLEX WITH THE GUANINE NUCLEOTIDE EXCHANGE REGION OF TIAM1 1h10 
HIGH RESOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE PLECKSTRIN HOMOLOGY DOMAIN OF PROTEIN KINASE B/AKT BOUND TO INS(1,3,4,5)-TETRAKISPHOPHATE 1ki1 
Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Region of Intersectin in Complex with Cdc42 1kz7 
Crystal Structure of the DH/PH Fragment of Murine Dbs in Complex with the Placental Isoform of Human Cdc42 1kzg 
DbsCdc42(Y889F) 1lb1 
Crystal Structure of the Dbl and Pleckstrin homology domains of Dbs in complex with RhoA 1mai 
STRUCTURE OF THE PLECKSTRIN HOMOLOGY DOMAIN FROM PHOSPHOLIPASE C DELTA IN COMPLEX WITH INOSITOL TRISPHOSPHATE 1mph 
PLECKSTRIN HOMOLOGY DOMAIN FROM MOUSE BETA-SPECTRIN, NMR, 50 STRUCTURES 1nty 
Crystal structure of the first DH/PH domain of Trio to 1.7 A 1omw 
Crystal Structure of the complex between G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 and Heterotrimeric G Protein beta 1 and gamma 2 subunits 1p6s 
Solution Structure of the Pleckstrin Homology Domain of Human Protein Kinase B beta (Pkb/Akt) 1pls 
SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF A PLECKSTRIN HOMOLOGY DOMAIN 1pms 
PLECKSTRIN HOMOLOGY DOMAIN OF SON OF SEVENLESS 1 (SOS1) WITH GLYCINE-SERINE ADDED TO THE N-TERMINUS, NMR, 20 STRUCTURES 1qqg 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE PH-PTB TARGETING REGION OF IRS-1 1rj2 
Crystal structure of the DH/PH fragment of Dbs without bound GTPase 1txd 
Crystal Structure of the DH/PH domains of Leukemia-associated RhoGEF 1u27 
Triglycine variant of the ARNO Pleckstrin Homology Domain in complex with Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 1u29 
Triglycine variant of the ARNO Pleckstrin Homology Domain in complex with Ins(1,4,5)P3 1u2b 
Triglycine variant of the Grp1 Pleckstrin Homology Domain unliganded 1u5d 
Crystal Structure of the PH domain of SKAP55 1u5e 
Crystal Structure of a N-terminal Fragment of SKAP-Hom Containing Both the Helical Dimerization Domain and the PH Domain 1u5f 
Crystal Structure of the PH Domain of SKAP-Hom with 8 Vector-derived N-terminal Residues 1u5g 
Crystal Structure of the PH Domain of SKAP-Hom 1unp 
Crystal structure of the pleckstrin homology domain of PKB alpha 1unq 
High resolution crystal structure of the Pleckstrin Homology Domain Of Protein Kinase B/Akt Bound To Ins(1,3,4,5)-Tetrakisphophate 1unr 
Crystal structure of the PH domain of PKB alpha in complex with a sulfate molecule 1upq 
Crystal structure of the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of PEPP1 1upr 
Crystal structure of the PEPP1 pleckstrin homology domain in complex with Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate 1v5m 
Solution Structure of the Pleckstrin Homology Domain of Mouse APS 1v5p 
Solution Structure of the N-terminal Pleckstrin Homology Domain Of TAPP2 from Mouse 1v5u 
Solution Structure of the C-terminal Pleckstrin Homology Domain of Sbf1 from Mouse 1v61 
Solution Structure of the Pleckstrin Homology Domain of alpha-Pix 1v88 
Solution Structure of the Pleckstrin Homology Domain of Oxysterol-Binding Protein-Related Protein 8 (KIAA1451 Protein) 1v89 
Solution Structure of the Pleckstrin Homology Domain of Human KIAA0053 Protein 1wg7 
Solution structure of pleckstrin homology domain from human KIAA1058 protein 1wgq 
Solution Structure of the Pleckstrin Homology Domain of Mouse Ethanol Decreased 4 Protein 1wi1 
Solution structure of the PH domain of human calcium-dependent activator protein for secretion (CAPS) 1wjm 
Solution structure of pleckstrin homology domain of human beta III spectrin. 1x05 
Solution structure of the C-terminal PH domain of human pleckstrin 1x1f 
Solution structure of the PH domain of human Docking protein BRDG1 1x1g 
Solution structure of the C-terminal PH domain of human pleckstrin 2 1x86 
Crystal Structure of the DH/PH domains of Leukemia-associated RhoGEF in complex with RhoA 1xcg 
Crystal Structure of Human RhoA in complex with DH/PH fragment of PDZRHOGEF 1xd4 
Crystal structure of the DH-PH-cat module of Son of Sevenless (SOS) 1xdv 
Experimentally Phased Structure of Human the Son of Sevenless protein at 4.1 Ang. 1xx0 
Structure of the C-terminal PH domain of human pleckstrin 1ym7 
G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 (GRK2) 1zc3 
Crystal structure of the Ral-binding domain of Exo84 in complex with the active RalA 1zc4 
Crystal structure of the Ral-binding domain of Exo84 in complex with the active RalA 1zm0 
Crystal Structure of the Carboxyl Terminal PH Domain of Pleckstrin To 2.1 Angstroms 2adz 
solution structure of the joined PH domain of alpha1-syntrophin 2bcj 
Crystal Structure of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 in Complex with Galpha-q and Gbetagamma Subunits 2coa 
Solution structure of the PH domain of protein kinase C, D2 type from human 2coc 
Solution structure of the C-terminal PH domain of FYVE, RhoGEF and PH domain containing protein 3 (FGD3) from human 2cod 
Solution structure of the N-terminal PH domain of ARAP2 protein from human 2cof 
Solution structure of the C-terminal PH domain of hypothetical protein KIAA1914 from human 2d9v 
Solution structure of the PH domain of Pleckstrin homology domain-containing protein family B member 1 from mouse 2d9w 
Solution structure of the PH domain of Docking protein 2 from human 2d9x 
Solution structure of the PH domain of Oxysterol binding protein-related protein 11 from human 2d9y 
Solution structure of the PH domain of PEPP-3 from human 2d9z 
Solution structure of the PH domain of Protein kinase C, nu type from human 2da0 
Solution structure of the PH domain of PIP2-dependent ARF1 GTPase-activating protein from human 2dfk 
Crystal structure of the CDC42-Collybistin II complex 2dhi 
Solution structure of the PH domain of Evectin-2 from mouse 2dhj 
Solution structure of the PH domain of Rho GTPase activating protein 21 from human 2dhk 
Solution structure of the PH domain of TBC1 domain family member 2 protein from human 2dkp 
Solution structure of the PH domain of pleckstrin homology domain-containing protein family A member 5 from human 2dn6 
Solution structure of the PH domain of KIAA0640 protein from human 2dtc 
Crystal structure of MS0666 2dx1 
Crystal structure of RhoGEF protein Asef 2dyn 
DYNAMIN (PLECKSTRIN HOMOLOGY DOMAIN) (DYNPH) 2elb 
Crystal Structure of the BAR-PH domain of human APPL1 2fjl 
Solution Structure of the Split PH domain in Phospholipase C-gamma1 2i5c 
Crystal structure of the C-terminal PH domain of pleckstrin in complex with D-myo-Ins(1,2,3,4,5)P5 2i5f 
Crystal structure of the C-terminal PH domain of pleckstrin in complex with D-myo-Ins(1,2,3,5,6)P5 2j59 
Crystal structure of the ARF1:ARHGAP10-ArfBD complex 2k2j 
NMR solution structure of the split PH domain from Phospholipase C gamma 2 2kcj 
solution structure of FAPP1 PH domain 2lg1 
Solution structure of the human AKAP13 PH domain and stabilizing DH helix 2lko 
Structural Basis of Phosphoinositide Binding to Kindlin-2 Pleckstrin Homology Domain in Regulating Integrin Activation 2lul 
Solution NMR Structure of PH Domain of Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec from Homo sapiens, Northeast Structural Genomics Consortium (NESG) Target HR3504C 2mdx 
2MDX 2nz8 
N-terminal DHPH cassette of Trio in complex with nucleotide-free Rac1 2otx 
Crystal Structure of A N-terminal Fragment of SKAP-HOM Containing both the Helical Dimerization Domain and the PH Domain 2p0d 
ArhGAP9 PH domain in complex with Ins(1,4,5)P3 2p0f 
ArhGAP9 PH domain in complex with Ins(1,3,5)P3 2p0h 
ArhGAP9 PH domain in complex with Ins(1,3,4)P3 2pz1 
Crystal Structure of Auto-inhibited Asef 2q13 
Crystal structure of BAR-PH domain of APPL1 2r09 
Crystal Structure of Autoinhibited Form of Grp1 Arf GTPase Exchange Factor 2r0d 
Crystal Structure of Autoinhibited Form of Grp1 Arf GTPase Exchange Factor 2rgn 
Crystal Structure of p63RhoGEF complex with Galpha-q and RhoA 2rlo 
Split PH domain of PI3-kinase enhancer 2rov 
The split PH domain of ROCK II 2rsg 
Solution structure of the CERT PH domain 2uvm 
Structure of PKBalpha PH domain in complex with a novel inositol headgroup surrogate, benzene 1,2,3,4-tetrakisphosphate 2uzr 
A transforming mutation in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1 in cancer (AKT1-PH_E17K) 2uzs 
A transforming mutation in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1 in cancer (AKT1-PH_E17K) 2vrw 
Critical structural role for the PH and C1 domains of the Vav1 exchange factor 2w2w 
PLCg2 Split Pleckstrin Homology (PH) Domain 2w2x 
Complex of Rac2 and PLCg2 spPH Domain 2x18 
The crystal structure of the PH domain of human AKT3 protein kinase 2y7b 
Crystal structure of the PH domain of human Actin-binding protein anillin ANLN 2yry 
Solution structure of the PH domain of Pleckstrin homology domain-containing family A member 6 from human 2ys1 
Solution structure of the PH domain of Dynamin-2 from human 2ys3 
Solution structure of the PH domain of Kindlin-3 from human 2z0o 
Crystal structure of APPL1-BAR-PH domain 2z0p 
Crystal structure of PH domain of Bruton's tyrosine kinase 2z0q 
Crystal structure of DH-PH domain of RhoGEF3(Xpln) 3a8n 
Crystal structure of the Tiam1 PHCCEx domain 3a8p 
Crystal structure of the Tiam2 PHCCEx domain 3a8q 
Low-resolution crystal structure of the Tiam2 PHCCEx domain 3a98 
Crystal structure of the complex of the interacting regions of DOCK2 and ELMO1 3aj4 
Crystal structure of the PH domain of Evectin-2 from human complexed with O-phospho-L-serine 3bji 
Structural Basis of Promiscuous Guanine Nucleotide Exchange by the T-Cell Essential Vav1 3cik 
Human GRK2 in Complex with Gbetagamma subunits 3cxb 
Crystal Structure of sifa and skip 3feh 
Crystal structure of full length centaurin alpha-1 3fm8 
Crystal structure of full length centaurin alpha-1 bound with the FHA domain of KIF13B (CAPRI target) 3hk0 
Crystal Structure of the RA and PH Domains of Grb10 3hw2 
Crystal structure of the SifA-SKIP(PH) complex 3jzy 
Crystal structure of human Intersectin 2 C2 domain 3krw 
Human GRK2 in complex with Gbetgamma subunits and balanol (soak) 3krx 
Human GRK2 in complex with Gbetgamma subunits and balanol (co-crystal) 3ksy 
Crystal structure of the Histone domain, DH-PH unit, and catalytic unit of the Ras activator Son of Sevenless (SOS) 3ky9 
Autoinhibited Vav1 3kz1 
Crystal Structure of the Complex of PDZ-RhoGEF DH/PH domains with GTP-gamma-S Activated RhoA 3lju 
Crystal structure of full length centaurin alpha-1 bound with the head group of PIP3 3mdb 
Crystal structure of the ternary complex of full length centaurin alpha-1, KIF13B FHA domain, and IP4 3ml4 
Crystal structure of a complex between Dok7 PH-PTB and the MuSK juxtamembrane region 3mpx 
Crystal structure of the DH and PH-1 domains of human FGD5 3nsu 
A Systematic Screen for Protein-Lipid Interactions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae 3o96 
Crystal Structure of Human AKT1 with an Allosteric Inhibitor 3odo 
Crystal Structure of the DH/PH Domains of p115-RhoGEF 3odw 
Crystal Structure of the Linker-DH/PH domains of p115-RhoGEF 3odx 
Crystal Structure of an N-terminally Truncated Linker-DH/PH Domains of p115-RhoGEF 3p6a 
Crystal Structure of the DH/PH domains of p115-RhoGEF (R399E mutant) 3pp2 
Crystal structure of the pleckstrin homology domain of ArhGAP27 3psc 
Bovine GRK2 in complex with Gbetagamma subunits 3pvu 
Bovine GRK2 in complex with Gbetagamma subunits and a selective kinase inhibitor (CMPD101) 3pvw 
Bovine GRK2 in complex with Gbetagamma subunits and a selective kinase inhibitor (CMPD103A) 3qbv 
Structure of designed orthogonal interaction between CDC42 and nucleotide exchange domains of intersectin 3qr0 
Crystal Structure of S. officinalis PLC21 3qr1 
Crystal Structure of L. pealei PLC21 3qwm 
Crystal Structure of GEP100, the plextrin homology domain of IQ motif and SEC7 domain-containing protein 1 isoform a 3rcp 
Crystal structure of the FAPP1 pleckstrin homology domain 3snh 
Crystal structure of nucleotide-free human dynamin1 3t06 
Crystal Structure of the DH/PH fragment of PDZRHOGEF with N-terminal regulatory elements in complex with Human RhoA 3tca 
Crystal structure of the Ras-associating and pleckstrin-homology domains of RIAM 3tfm 
Myosin X PH1N-PH2-PH1C tandem 3uzs 
Structure of the C13.28 RNA Aptamer Bound to the G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2-Heterotrimeric G Protein Beta 1 and Gamma 2 Subunit Complex 3uzt 
Structure of the C13.18 RNA Aptamer in Complex with G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 3v5w 
Human G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 in Complex with Soluble Gbetagamma Subunits and Paroxetine 3via 
Crystal structure of the PH domain of Evectin-2 from human 3zvr 
Crystal structure of Dynamin 3zys 
Human dynamin 1 deltaPRD polymer stabilized with GMPPCP 4a5k 
Structural analyses of Slm1-PH domain demonstrate ligand binding in the non-canonical site 4a6f 
Crystal structure of Slm1-PH domain in complex with Phosphoserine 4a6h 
Crystal structure of Slm1-PH domain in complex with Inositol-4- phosphate 4a6k 
Crystal structure of Slm1-PH domain in complex with D-myo-Inositol-4- phosphate 4bbk 
Structural and functional characterisation of the kindlin-1 pleckstrin homology domain 4c0a 
Arf1(Delta1-17)in complex with BRAG2 Sec7-PH domain 4ckg 
4CKG 4ckh 
4CKH 4d0n 
AKAP13 (AKAP-Lbc) RhoGEF domain in complex with RhoA 4ejn 
Crystal structure of autoinhibited form of AKT1 in complex with N-(4-(5-(3-acetamidophenyl)-2-(2-aminopyridin-3-yl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yl)benzyl)-3-fluorobenzamide 4f7h 
The crystal structure of kindlin-2 pleckstrin homology domain in free form 4gmv 
Crystal Structure of the coiled-coil, RA and PH domains of Lamellipodin 4gn1 
Crystal Structure of the RA and PH domains of Lamellipodin 4gzu 
Crystal strucure of the DH-PH-PH domain of FARP2 4h6y 
Crystal strucure of the DH-PH-PH domain of FARP1 4h8s 
Crystal structure of human APPL2BARPH domain 4hhv 
Crystal structure of ceramide transfer protein pleckstrin homology domain 4iap 
Crystal structure of PH domain of Osh3 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae 4k2o 
The Structure of a Triple Mutant of the Tiam1 PH-CC-Ex Domain 4k2p 
The Structure of a Quintuple Mutant of the Tiam1 PH-CC-Ex Domain 4k81 
Crystal structure of the Grb14 RA and PH domains in complex with GTP-loaded H-Ras 4kax 
Crystal structure of the Grp1 PH domain in complex with Arf6-GTP 4kvg 
Crystal structure of RIAM RA-PH domains in complex with GTP bound Rap1 4mk0 
Crystal structure of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in complex with a a rationally designed paroxetine derivative 4mt6 
4MT6 4mt7 
4MT7 4nsw 
4NSW 4pnk 
4PNK 4uud 
4UUD 4uuk 
4UUK 4xh3 
4XH3 4xh9 
4XH9 4xoh 
4XOH 4y93 
4Y93 4y94 
4Y94 4yon 
4YON 5a3f 
5A3F 5c5b 
5C5B 5c6r 
5C6R 5c79 
5C79 5d27 
5D27 5d3v 
5D3V 5d3w 
5D3W 5d3x 
5D3X 5d3y 
5D3Y 5efx 
5EFX 5fi0 
5FI0 5fi1 
5FI1 5he0 
5HE0 5he1 
5HE1 5he2 
5HE2 5he3 
5HE3 5kcv 
5KCV - Links (links to other resources describing this domain)
-
PROSITE PH_DOMAIN PFAM PH INTERPRO IPR001849

