The domain within your query sequence starts at position 1 and ends at position 158; the E-value for the VWA domain shown below is 4.11e-1.
MPILLFLIDTSASMNQRSHLGTTYLDTAKGAVETFMKLRARDPASRGDRYMLVTFEEPPY AIKAGWKENHATFMNELKNLQAEGLTTLGQSLRTAFDLLNLNRLVTGIDNYGQGRNPFFL EPAIIITITDGSKLTTTSGVQDELHLPLNSPLPGSELT
VWAvon Willebrand factor (vWF) type A domain |
|---|
| SMART accession number: | SM00327 |
|---|---|
| Description: | VWA domains in extracellular eukaryotic proteins mediate adhesion via metal ion-dependent adhesion sites (MIDAS). Intracellular VWA domains and homologues in prokaryotes have recently been identified. The proposed VWA domains in integrin beta subunits have recently been substantiated using sequence-based methods. |
| Interpro abstract (IPR002035): | The von Willebrand factor is a large multimeric glycoprotein found in blood plasma. Mutant forms are involved in the aetiology of bleeding disorders [ (PUBMED:8440408) ]. In von Willebrand factor, the type A domain (vWF) is the prototype for a protein superfamily. The vWF domain is found in various plasma proteins: complement factors B, C2, CR3 and CR4; the integrins (I-domains); collagen types VI, VII, XII and XIV; and other extracellular proteins [ (PUBMED:8412987) (PUBMED:8145250) (PUBMED:1864378) ]. Although the majority of VWA-containing proteins are extracellular, the most ancient ones present in all eukaryotes are all intracellular proteins involved in functions such as transcription, DNA repair, ribosomal and membrane transport and the proteasome. A common feature appears to be involvement in multiprotein complexes. Proteins that incorporate vWF domains participate in numerous biological events (e.g. cell adhesion, migration, homing, pattern formation, and signal transduction), involving interaction with a large array of ligands [ (PUBMED:8412987) ]. A number of human diseases arise from mutations in VWA domains. Secondary structure prediction from 75 aligned vWF sequences has revealed a largely alternating sequence of alpha-helices and beta-strands [ (PUBMED:8145250) ]. The vWF domain fold is predicted to be a doubly-wound, open, twisted beta-sheet flanked by alpha-helices [ (PUBMED:7843416) ]. 3D structures have been determined for the I-domains of integrins alpha-M (CD11b; with bound magnesium) [ (PUBMED:7867070) ] and alpha-L (CD11a; with bound manganese) [ (PUBMED:7479767) ]. The domain adopts a classic alpha/beta Rossmann fold and contains an unusual metal ion coordination site at its surface. It has been suggested that this site represents a general metal ion-dependent adhesion site (MIDAS) for binding protein ligands [ (PUBMED:7867070) ]. The residues constituting the MIDAS motif in the CD11b and CD11a I-domains are completely conserved, but the manner in which the metal ion is coordinated differs slightly [ (PUBMED:7479767) ]. |
| Family alignment: |
There are 189281 VWA domains in 166516 proteins in SMART's nrdb database.
Click on the following links for more information.
- Evolution (species in which this domain is found)
-
Taxonomic distribution of proteins containing VWA domain.
This tree includes only several representative species. The complete taxonomic breakdown of all proteins with VWA domain is also avaliable.
Click on the protein counts, or double click on taxonomic names to display all proteins containing VWA domain in the selected taxonomic class.
- Cellular role (predicted cellular role)
-
Binding / catalysis: Divalent cations.
- Literature (relevant references for this domain)
-
Primary literature is listed below; Automatically-derived, secondary literature is also avaliable.
- Ponting CP, Aravind L, Schultz J, Bork P, Koonin EV
- Eukaryotic signalling domain homologues in archaea and bacteria. Ancient ancestry and horizontal gene transfer.
- J Mol Biol. 1999; 289: 729-45
- Display abstract
Phyletic distributions of eukaryotic signalling domains were studied using recently developed sensitive methods for protein sequence analysis, with an emphasis on the detection and accurate enumeration of homologues in bacteria and archaea. A major difference was found between the distributions of enzyme families that are typically found in all three divisions of cellular life and non-enzymatic domain families that are usually eukaryote-specific. Previously undetected bacterial homologues were identified for# plant pathogenesis-related proteins, Pad1, von Willebrand factor type A, src homology 3 and YWTD repeat-containing domains. Comparisons of the domain distributions in eukaryotes and prokaryotes enabled distinctions to be made between the domains originating prior to the last common ancestor of all known life forms and those apparently originating as consequences of horizontal gene transfer events. A number of transfers of signalling domains from eukaryotes to bacteria were confidently identified, in contrast to only a single case of apparent transfer from eukaryotes to archaea.
- Baldwin ET et al.
- Cation binding to the integrin CD11b I domain and activation model assessment.
- Structure. 1998; 6: 923-35
- Display abstract
BACKGROUND: The integrin family of cell-surface receptors mediate cell adhesion through interactions with the extracellular matrix or other cell-surface receptors. The alpha chain of some integrin heterodimers includes an inserted 'I domain' of about 200 amino acids which binds divalent metal ions and is essential for integrin function. Lee et al. proposed that the I domain of the integrin CD11b adopts a unique 'active' conformation when bound to its counter receptor. In addition, they proposed that the lack of adhesion in the presence of Ca2+ ion reflected the stabilization of an 'inactive' I-domain conformation. We set out to independently determine the structure of the CD11 b I domain and to evaluate the structural effects of divalent ion binding to this protein. RESULTS: We have determined the X-ray structure of a new crystal form of the CD11 b I domain in the absence of added metal ions by multiple isomorphous replacement (MIR). Metal ions were easily introduced into this crystal form allowing the straight-forward assessment of the structural effects of divalent cation binding at the metal ion dependent adhesion site (MIDAS). The equilibrium binding constants for these ions were determined by titration calorimetry. The overall protein conformation and metal-ion coordination of the I domain is the same as that observed for all previously reported CD11 a I-domain structures and a CD11 b I-domain complex with Mn2+. These structures define a majority conformation. CONCLUSIONS: Addition of the cations Mg2+, Mn2+ and Cd2+ to the metal-free I domain does not induce conformational changes in the crystalline environment. Moreover, we find that Ca2+ binds poorly to the I domain which serves to explain its failure to support adhesion. We show that the active conformation proposed by Lee et al, is likely to be a construct artifact and we propose that the currently available data do not support a dramatic structural transition for the I domain during counter-receptor binding.
- Sadler JE
- Biochemistry and genetics of von Willebrand factor.
- Annu Rev Biochem. 1998; 67: 395-424
- Display abstract
Von Willebrand factor (VWF) is a blood glycoprotein that is required for normal hemostasis, and deficiency of VWF, or von Willebrand disease (VWD), is the most common inherited bleeding disorder. VWF mediates the adhesion of platelets to sites of vascular damage by binding to specific platelet membrane glycoproteins and to constituents of exposed connective tissue. These activities appear to be regulated by allosteric mechanisms and possibly by hydrodynamic shear forces. VWF also is a carrier protein for blood clotting factor VIII, and this interaction is required for normal factor VIII survival in the circulation. VWF is assembled from identical approximately 250 kDa subunits into disulfide-linked multimers that may be > 20,000 kDa. Mutations in VWD can disrupt this complex biosynthetic process at several steps to impair the assembly, intracellular targeting, or secretion of VWF multimers. Other VWD mutations impair the survival of VWF in plasma or the function of specific ligand binding sites. This growing body of information about VWF synthesis, structure, and function has allowed the reclassification of VWD based upon distinct pathophysiologic mechanisms that appear to correlate with clinical symptoms and the response to therapy.
- Disease (disease genes where sequence variants are found in this domain)
-
SwissProt sequences and OMIM curated human diseases associated with missense mutations within the VWA domain.
Protein Disease Collagen alpha-1(VII) chain (Q02388) (SMART) OMIM:120120: Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica, dominant
OMIM:131750: Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica, recessive
OMIM:226600: Epidermolysis bullosa, pretibial, dominant and recessive
OMIM:131850:Collagen alpha-3(VI) chain (P12111) (SMART) OMIM:120250: Bethlem myopathy
OMIM:158810:von Willebrand factor (P04275) (SMART) OMIM:193400: von Willebrand disease - Metabolism (metabolic pathways involving proteins which contain this domain)
-
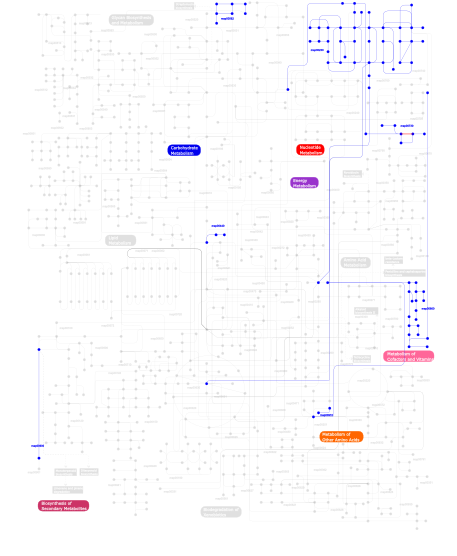
Click the image to view the interactive version of the map in iPath% proteins involved KEGG pathway ID Description 16.10 map04810 Regulation of actin cytoskeleton 14.88  map00860
map00860Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism 14.75 map04510 Focal adhesion 14.75 map04512 ECM-receptor interaction 5.68 map04514 Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) 4.19 map04670 Leukocyte transendothelial migration 3.92 map04640 Hematopoietic cell lineage 3.52 map04740 Olfactory transduction 3.11 map03022 Basal transcription factors 2.98 map04010 MAPK signaling pathway 2.71  map00910
map00910Nitrogen metabolism 2.57 map05222 Small cell lung cancer 2.44 map04610 Complement and coagulation cascades 2.30 map03050 Proteasome 2.03 map04650 Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity 1.49 map04360 Axon guidance 0.95 map03090 Type II secretion system 0.41  map00562
map00562Inositol phosphate metabolism 0.41 map04070 Phosphatidylinositol signaling system 0.27  map00440
map00440Aminophosphonate metabolism 0.27  map00900
map00900Terpenoid biosynthesis 0.14  map00730
map00730Thiamine metabolism 0.14  map00230
map00230Purine metabolism This information is based on mapping of SMART genomic protein database to KEGG orthologous groups. Percentage points are related to the number of proteins with VWA domain which could be assigned to a KEGG orthologous group, and not all proteins containing VWA domain. Please note that proteins can be included in multiple pathways, ie. the numbers above will not always add up to 100%.
- Structure (3D structures containing this domain)
3D Structures of VWA domains in PDB
PDB code Main view Title 1ao3 
A3 DOMAIN OF VON WILLEBRAND FACTOR 1aox 
I DOMAIN FROM INTEGRIN ALPHA2-BETA1 1atz 
HUMAN VON WILLEBRAND FACTOR A3 DOMAIN 1auq 
A1 DOMAIN OF VON WILLEBRAND FACTOR 1bho 
MAC-1 I DOMAIN MAGNESIUM COMPLEX 1bhq 
MAC-1 I DOMAIN CADMIUM COMPLEX 1ck4 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF RAT A1B1 INTEGRIN I-DOMAIN. 1cqp 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE ANALYSIS OF THE COMPLEX LFA-1 (CD11A) I-DOMAIN / LOVASTATIN AT 2.6 A RESOLUTION 1dgq 
NMR SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE INSERTED DOMAIN OF HUMAN LEUKOCYTE FUNCTION ASSOCIATED ANTIGEN-1 1dzi 
integrin alpha2 I domain / collagen complex 1fe8 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE VON WILLEBRAND FACTOR A3 DOMAIN IN COMPLEX WITH A FAB FRAGMENT OF IGG RU5 THAT INHIBITS COLLAGEN BINDING 1fns 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE VON WILLEBRAND FACTOR (VWF) A1 DOMAIN I546V MUTANT IN COMPLEX WITH THE FUNCTION BLOCKING FAB NMC4 1idn 
MAC-1 I DOMAIN METAL FREE 1ido 
I-DOMAIN FROM INTEGRIN CR3, MG2+ BOUND 1ijb 
The von Willebrand Factor mutant (I546V) A1 domain 1ijk 
The von Willebrand Factor mutant (I546V) A1 domain-botrocetin Complex 1jeq 
Crystal Structure of the Ku Heterodimer 1jey 
Crystal Structure of the Ku heterodimer bound to DNA 1jlm 
I-DOMAIN FROM INTEGRIN CR3, MN2+ BOUND 1jv2 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE EXTRACELLULAR SEGMENT OF INTEGRIN ALPHAVBETA3 1l5g 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE EXTRACELLULAR SEGMENT OF INTEGRIN AVB3 IN COMPLEX WITH AN ARG-GLY-ASP LIGAND 1lfa 
CD11A I-DOMAIN WITH BOUND MN++ 1m10 
Crystal structure of the complex of Glycoprotein Ib alpha and the von Willebrand Factor A1 Domain 1m1u 
AN ISOLEUCINE-BASED ALLOSTERIC SWITCH CONTROLS AFFINITY AND SHAPE SHIFTING IN INTEGRIN CD11B A-DOMAIN 1m1x 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE EXTRACELLULAR SEGMENT OF INTEGRIN ALPHA VBETA3 BOUND TO MN2+ 1m2o 
Crystal Structure of the Sec23-Sar1 complex 1m2v 
Crystal Structure of the yeast Sec23/24 heterodimer 1mf7 
INTEGRIN ALPHA M I DOMAIN 1mhp 
Crystal structure of a chimeric alpha1 integrin I-domain in complex with the Fab fragment of a humanized neutralizing antibody 1mjn 
Crystal Structure of the intermediate affinity aL I domain mutant 1mq8 
Crystal structure of alphaL I domain in complex with ICAM-1 1mq9 
Crystal structure of high affinity alphaL I domain with ligand mimetic crystal contact 1mqa 
Crystal structure of high affinity alphaL I domain in the absence of ligand or metal 1n3y 
Crystal structure of the alpha-X beta2 integrin I domain 1n9z 
INTEGRIN ALPHA M I DOMAIN MUTANT 1na5 
INTEGRIN ALPHA M I DOMAIN 1oak 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE VON WILLEBRAND FACTOR (VWF) A1 DOMAIN IN COMPLEX WITH THE FUNCTION BLOCKING NMC-4 FAB 1pt6 
I domain from human integrin alpha1-beta1 1q0p 
A domain of Factor B 1qc5 
I Domain from Integrin Alpha1-Beta1 1qcy 
THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE I-DOMAIN OF HUMAN INTEGRIN ALPHA1BETA1 1rd4 
An allosteric inhibitor of LFA-1 bound to its I-domain 1rrk 
Crystal Structure Analysis of the Bb segment of Factor B 1rs0 
Crystal Structure Analysis of the Bb segment of Factor B complexed with Di-isopropyl-phosphate (DIP) 1rtk 
Crystal Structure Analysis of the Bb segment of Factor B complexed with 4-guanidinobenzoic acid 1sht 
Crystal Structure of the von Willebrand factor A domain of human capillary morphogenesis protein 2: an anthrax toxin receptor 1shu 
Crystal Structure of the von Willebrand factor A domain of human capillary morphogenesis protein 2: an anthrax toxin receptor 1sq0 
Crystal Structure of the Complex of the Wild-type Von Willebrand Factor A1 domain and Glycoprotein Ib alpha at 2.6 Angstrom Resolution 1t0p 
Structural Basis of ICAM recognition by integrin alpahLbeta2 revealed in the complex structure of binding domains of ICAM-3 and alphaLbeta2 at 1.65 A 1t6b 
Crystal structure of B. anthracis Protective Antigen complexed with human Anthrax toxin receptor 1tye 
Structural basis for allostery in integrins and binding of ligand-mimetic therapeutics to the platelet receptor for fibrinogen 1tzn 
Crystal Structure of the Anthrax Toxin Protective Antigen Heptameric Prepore bound to the VWA domain of CMG2, an anthrax toxin receptor 1u0n 
The ternary von Willebrand Factor A1-glycoprotein Ibalpha-botrocetin complex 1u0o 
The mouse von Willebrand Factor A1-botrocetin complex 1u8c 
A novel adaptation of the integrin PSI domain revealed from its crystal structure 1uex 
Crystal structure of von Willebrand Factor A1 domain complexed with snake venom bitiscetin 1v7p 
Structure of EMS16-alpha2-I domain complex 1xdd 
X-ray structure of LFA-1 I-domain in complex with LFA703 at 2.2A resolution 1xdg 
X-ray structure of LFA-1 I-domain in complex with LFA878 at 2.1A resolution 1xuo 
X-ray structure of LFA-1 I-domain bound to a 1,4-diazepane-2,5-dione inhibitor at 1.8A resolution 1zon 
CD11A I-DOMAIN WITHOUT BOUND CATION 1zoo 
CD11A I-DOMAIN WITH BOUND MAGNESIUM ION 1zop 
CD11A I-DOMAIN WITH BOUND MAGNESIUM ION 2adf 
Crystal Structure and Paratope Determination of 82D6A3, an Antithrombotic Antibody Directed Against the von Willebrand factor A3-Domain 2b2x 
VLA1 RdeltaH I-domain complexed with a quadruple mutant of the AQC2 Fab 2i6q 
Complement component C2a 2i6s 
Complement component C2a 2ica 
CD11a (LFA1) I-domain complexed with BMS-587101 aka 5-[(5S, 9R)-9-(4-cyanophenyl)-3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-1-methyl-2,4-dioxo-1,3,7-triazaspiro [4.4]non-7-yl]methyl]-3-thiophenecarboxylicacid 2iue 
Pactolus I-domain: Functional Switching of the Rossmann Fold 2m32 
Alpha-1 integrin I-domain in complex with GLOGEN triple helical peptide 2o7n 
CD11A (LFA1) I-domain complexed with 7A-[(4-cyanophenyl)methyl]-6-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-5-oxo-2,3,5,7A-tetrahydro-1H-pyrrolo[1,2-A]pyrrole-7-carbonitrile 2odp 
Complement component C2a, the catalytic fragment of C3- and C5-convertase of human complement 2odq 
Complement component C2a, the catalytic fragment of C3- and C5-convertase of human complement 2ok5 
Human Complement factor B 2qtv 
Structure of Sec23-Sar1 complexed with the active fragment of Sec31 2vc2 
Re-refinement of Integrin AlphaIIbBeta3 Headpiece Bound to Antagonist L-739758 2vdk 
Re-refinement of Integrin AlphaIIbBeta3 Headpiece 2vdl 
Re-refinement of Integrin AlphaIIbBeta3 Headpiece 2vdm 
Re-refinement of Integrin AlphaIIbBeta3 Headpiece Bound to Antagonist Tirofiban 2vdn 
Re-refinement of Integrin AlphaIIbBeta3 Headpiece Bound to Antagonist Eptifibatide 2vdo 
Integrin AlphaIIbBeta3 Headpiece Bound to Fibrinogen Gamma chain peptide, HHLGGAKQAGDV 2vdp 
Integrin AlphaIIbBeta3 Headpiece Bound to Fibrinogen Gamma chain peptide,LGGAKQAGDV 2vdq 
Integrin AlphaIIbBeta3 Headpiece Bound to a Chimeric Fibrinogen Gamma chain peptide, HHLGGAKQRGDV 2vdr 
Integrin AlphaIIbBeta3 Headpiece Bound to Fibrinogen Gamma chain chimera peptide, LGGAKQRGDV 2win 
C3 convertase (C3bBb) stabilized by SCIN 2ww8 
Structure of the pilus adhesin (RrgA) from Streptococcus pneumoniae 2x31 
Modelling of the complex between subunits BchI and BchD of magnesium chelatase based on single-particle cryo-EM reconstruction at 7.5 ang 2x5n 
Crystal Structure of the SpRpn10 VWA domain 2xgg 
Structure of Toxoplasma gondii Micronemal Protein 2 A_I Domain 2xwb 
Crystal Structure of Complement C3b in complex with Factors B and D 2xwj 
Crystal Structure of Complement C3b in Complex with Factor B 3bn3 
crystal structure of ICAM-5 in complex with aL I domain 3bqm 
LFA-1 I domain bound to inhibitors 3bqn 
LFA-1 I domain bound to inhibitors 3e2m 
LFA-1 I domain bound to inhibitors 3eoa 
Crystal structure the Fab fragment of Efalizumab in complex with LFA-1 I domain, Form I 3eob 
Crystal structure the Fab fragment of Efalizumab in complex with LFA-1 I domain, Form II 3f74 
Crystal structure of wild type LFA1 I domain 3f78 
Crystal structure of wild type LFA1 I domain complexed with isoflurane 3fcs 
Structure of complete ectodomain of integrin aIIBb3 3fcu 
Structure of headpiece of integrin aIIBb3 in open conformation 3gxb 
Crystal structure of VWF A2 domain 3hi6 
Crystal structure of intermediate affinity I domain of integrin LFA-1 with the Fab fragment of its antibody AL-57 3hrz 
Cobra Venom Factor (CVF) in complex with human factor B 3hs0 
Cobra Venom Factor (CVF) in complex with human factor B 3hxo 
Crystal Structure of Von Willebrand Factor (VWF) A1 Domain in Complex with DNA Aptamer ARC1172, an Inhibitor of VWF-Platelet Binding 3hxq 
Crystal Structure of Von Willebrand Factor (VWF) A1 Domain in Complex with DNA Aptamer ARC1172, an Inhibitor of VWF-Platelet Binding 3ibs 
Crystal structure of conserved hypothetical protein BatB from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 3ije 
Crystal structure of the complete integrin alhaVbeta3 ectodomain plus an Alpha/beta transmembrane fragment 3jbr 
3JBR 3jco 
3JCO 3jcp 
3JCP 3k6s 
Structure of integrin alphaXbeta2 ectodomain 3k71 
Structure of integrin alphaX beta2 ectodomain 3k72 
Structure of integrin alphaX beta2 3m6f 
CD11A I-domain complexed with 6-((5S,9R)-9-(4-CYANOPHENYL)-3-(3,5-DICHLOROPHENYL)-1-METHYL-2,4-DIOXO-1,3,7- TRIAZASPIRO[4.4]NON-7-YL)NICOTINIC ACID 3n2n 
The Crystal Structure of Tumor Endothelial Marker 8 (TEM8) extracellular domain 3nid 
The Closed Headpiece of Integrin alphaIIB beta3 and its Complex with an alpahIIB beta3 -Specific Antagonist That Does Not Induce Opening 3nif 
The Closed Headpiece of Integrin IIb 3 and its Complex with an IIb 3 -Specific Antagonist That Does Not Induce Opening 3nig 
The Closed Headpiece of Integrin IIb 3 and its Complex with an IIb 3 -Specific Antagonist That Does Not Induce Opening 3ppv 
Crystal structure of an engineered VWF A2 domain (N1493C and C1670S) 3ppw 
Crystal structure of the D1596A mutant of an engineered VWF A2 domain (N1493C and C1670S) 3ppx 
Crystal structure of the N1602A mutant of an engineered VWF A2 domain (N1493C and C1670S) 3ppy 
Crystal structure of the D1596A/N1602A double mutant of an engineered VWF A2 domain (N1493C and C1670S) 3q3g 
Crystal Structure of A-domain in complex with antibody 3qa3 
Crystal Structure of A-domain in complex with antibody 3t3m 
A Novel High Affinity Integrin alphaIIbbeta3 Receptor Antagonist That Unexpectedly Displaces Mg2+ from the beta3 MIDAS 3t3p 
A Novel High Affinity Integrin alphaIIbbeta3 Receptor Antagonist That Unexpectedly Displaces Mg2+ from the beta3 MIDAS 3tcx 
Structure of Engineered Single Domain ICAM-1 D1 with High-Affinity aL Integrin I Domain of Native C-Terminal Helix Conformation 3tvy 
Structural Analysis of Adhesive Tip pilin, GBS104 from Group B Streptococcus agalactiae 3tw0 
Structural Analysis of Adhesive Tip pilin, GBS104 from Group B Streptococcus agalactiae 3txa 
Structural Analysis of Adhesive Tip pilin, GBS104 from Group B Streptococcus agalactiae 3v4p 
crystal structure of a4b7 headpiece complexed with Fab ACT-1 3v4v 
crystal structure of a4b7 headpiece complexed with Fab ACT-1 and RO0505376 3vi3 
Crystal structure of alpha5beta1 integrin headpiece (ligand-free form) 3vi4 
Crystal structure of alpha5beta1 integrin headpiece in complex with RGD peptide 3zdx 
Integrin alphaIIB beta3 headpiece and RGD peptide complex 3zdy 
Integrin alphaIIB beta3 headpiece and RGD peptide complex 3zdz 
Integrin alphaIIB beta3 headpiece and RGD peptide complex 3ze0 
Integrin alphaIIB beta3 headpiece and RGD peptide complex 3ze1 
Integrin alphaIIB beta3 headpiece and RGD peptide complex 3ze2 
Integrin alphaIIB beta3 headpiece and RGD peptide complex 3zqk 
Von Willebrand Factor A2 domain with calcium 4a0q 
Activated Conformation of Integrin alpha1 I-Domain mutant 4bj3 
Integrin alpha2 I domain E318W-collagen complex 4bzi 
The structure of the COPII coat assembled on membranes 4c29 
Crystal Structure of High-Affinity von Willebrand Factor A1 domain with Disulfide Mutation 4c2a 
Crystal Structure of High-Affinity von Willebrand Factor A1 domain with R1306Q and I1309V Mutations in Complex with High Affinity GPIb alpha 4c2b 
Crystal Structure of High-Affinity von Willebrand Factor A1 domain with Disulfide Mutation in Complex with High Affinity GPIb alpha 4cak 
Three-dimensional reconstruction of intact human integrin alphaIIbbeta3 in a phospholipid bilayer nanodisc 4cn8 
Structure of proximal thread matrix protein 1 (PTMP1) from the mussel byssus 4cn9 
structure of proximal thread matrix protein 1 (PTMP1) from the mussel byssus with zinc occupied MIDAS motif 4cnb 
Structure of proximal thread matrix protein 1 (PTMP1) from the mussel byssus - Crystal form 2 4cr2 
Deep classification of a large cryo-EM dataset defines the conformational landscape of the 26S proteasome 4cr3 
Deep classification of a large cryo-EM dataset defines the conformational landscape of the 26S proteasome 4cr4 
Deep classification of a large cryo-EM dataset defines the conformational landscape of the 26S proteasome 4dmu 
Crystal structure of the von Willebrand factor A3 domain in complex with a collagen III derived triple-helical peptide 4f1j 
Crystal structure of the MG2+ loaded VWA domain of plasmodium falciparum trap protein 4f1k 
Crystal structure of the MG2+ free VWA domain of plasmodium falciparum trap protein 4fx5 
von Willebrand factor type A from Catenulispora acidiphila 4g1e 
Crystal structure of integrin alpha V beta 3 with coil-coiled tag. 4g1m 
Re-refinement of alpha V beta 3 structure 4hqf 
Crystal structure of Plasmodium falciparum TRAP, I4 form 4hqk 
Crystal structure of Plasmodium falciparum TRAP, P4212 form 4hql 
Crystal structure of magnesium-loaded Plasmodium vivax TRAP protein 4hqn 
Crystal structure of manganese-loaded Plasmodium vivax TRAP protein 4hqo 
Crystal structure of Plasmodium vivax TRAP protein 4igi 
Crystal structure of the Collagen VI alpha3 N5 domain 4ihk 
Crystal structure of the Collagen VI alpha3 N5 domain R1061Q 4ixd 
X-ray structure of lfa-1 i-domain in complex with ibe-667 at 1.8a resolution 4jdu 
The crystal structure of an aerotolerance-related membrane protein from Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343 with multiple mutations to serines. 4m76 
Integrin I domain of complement receptor 3 in complex with C3d 4mmx 
Integrin AlphaVBeta3 ectodomain bound to the tenth domain of Fibronectin 4mmy 
Integrin AlphaVBeta3 ectodomain bound to the tenth domain of Fibronectin with the IAKGDWND motif 4mmz 
Integrin AlphaVBeta3 ectodomain bound to an antagonistic tenth domain of Fibronectin 4neh 
An internal ligand-bound, metastable state of a leukocyte integrin, aXb2 4nen 
An internal ligand-bound, metastable state of a leukocyte integrin, aXb2 4o02 
AlphaVBeta3 integrin in complex with monoclonal antibody FAB fragment. 4okr 
Structures of Toxoplasma gondii MIC2 4oku 
Structure of Toxoplasma gondii proMIC2 4rck 
4RCK 4um8 
4UM8 4um9 
4UM9 4wfq 
4WFQ 4wjk 
4WJK 4wk0 
4WK0 4wk2 
4WK2 4wk4 
4WK4 4xw2 
4XW2 4z7n 
4Z7N 4z7o 
4Z7O 4z7q 
4Z7Q 5a5b 
5A5B 5a8j 
5A8J 5bv8 
5BV8 5e6r 
5E6R 5e6s 
5E6S 5e6u 
5E6U 5es4 
5ES4 5fl8 
5FL8 5gjq 
5GJQ 5gjr 
5GJR 5gjv 
5GJV 5gjw 
5GJW 5hdb 
5HDB 5ivw 
5IVW 5iy6 
5IY6 5iy7 
5IY7 5iy8 
5IY8 5iy9 
5IY9 5jcs 
5JCS 5l4k 
5L4K 5ln1 
5LN1 5t0c 
5T0C 5t0g 
5T0G 5t0h 
5T0H 5t0i 
5T0I 5t0j 
5T0J - Links (links to other resources describing this domain)
-
PFAM vwa INTERPRO IPR002035

