The domain within your query sequence starts at position 412 and ends at position 451; the E-value for the WD40 domain shown below is 4.95e-4.
VWSRSIEDPARSAGFHPSGSVLAVGTVTGRWLLLDTETHD
WD40WD40 repeats |
|---|
| SMART accession number: | SM00320 |
|---|---|
| Description: | Note that these repeats are permuted with respect to the structural repeats (blades) of the beta propeller domain. |
| Interpro abstract (IPR001680): | WD-40 repeats (also known as WD or beta-transducin repeats) are short ~40 amino acid motifs, often terminating in a Trp-Asp (W-D) dipeptide. WD40 repeats usually assume a 7-8 bladed beta-propeller fold, but proteins have been found with 4 to 16 repeated units, which also form a circularised beta-propeller structure. WD-repeat proteins are a large family found in all eukaryotes and are implicated in a variety of functions ranging from signal transduction and transcription regulation to cell cycle control and apoptosis. Repeated WD40 motifs act as a site for protein-protein or protein-DNA interaction, and proteins containing WD40 repeats are known to serve as platforms for the assembly of protein complexes or mediators of transient interplay among other proteins [ (PUBMED:30069656) ]. The specificity of the proteins is determined by the sequences outside the repeats themselves. Examples of such complexes are G proteins (beta subunit is a beta-propeller), TAFII transcription factor, and E3 ubiquitin ligase [ (PUBMED:11814058) (PUBMED:10322433) ]. In Arabidopsis spp., several WD40-containing proteins act as key regulators of plant-specific developmental events. |
| GO function: | protein binding (GO:0005515) |
| Family alignment: |
There are 1918936 WD40 domains in 345139 proteins in SMART's nrdb database.
Click on the following links for more information.
- Evolution (species in which this domain is found)
-
Taxonomic distribution of proteins containing WD40 domain.
This tree includes only several representative species. The complete taxonomic breakdown of all proteins with WD40 domain is also avaliable.
Click on the protein counts, or double click on taxonomic names to display all proteins containing WD40 domain in the selected taxonomic class.
- Cellular role (predicted cellular role)
-
Cellular role: signalling
- Literature (relevant references for this domain)
-
Primary literature is listed below; Automatically-derived, secondary literature is also avaliable.
- Garcia-Higuera I et al.
- Folding of proteins with WD-repeats: comparison of six members of the WD-repeat superfamily to the G protein beta subunit.
- Biochemistry. 1996; 35: 13985-94
- Display abstract
The family of WD-repeat proteins comprises over 30 different proteins that share a highly conserved repeating motif [Neer, E. J., Schmidt, C. J., Nambudripad, R., & Smith, T. F. (1994) Nature 371, 297-300]. Members of this family include the signal-transducing G protein beta subunit, as well as other proteins that regulate signal transduction, transcription, pre-mRNA splicing, cytoskeletal organization, and vesicular fusion. The crystal structure of one WD-repeat protein (G beta) has now been solved (Wall et al., 1995; Sondek et al, 1996) and reveals that the seven repeating units form a circular, propeller-like structure with seven blades each made up of four beta strands. It is very likely that all WD-repeat proteins form a similar structure. If so, it will be possible to use information about important surface regions of one family member to predict properties of another. If WD proteins form structures similar to G beta, their hydrodynamic properties should be those of compact, globular proteins, and they should be resistant to cleavage by trypsin. However, the only studied example of a WD-repeat protein, G beta, synthesized in vitro in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate, is unable to fold into a native structure without its partner protein G gamma. The non-WD-repeat amino terminal alpha helix of G beta does not inhibit folding because G beta does not fold even when this region is removed. It is not known whether all WD-repeat proteins are unable to fold when synthesized in an in vitro system. We synthesized seven members of the family in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate, determined their Stokes radius, sedimentation coefficient, and frictional ratio, and assayed their stability to trypsin. Our working definition of folding was that the proteins from globular, trypsin-resistant structures because, except for G beta gamma, their functions are not known or cannot be assayed in reticulocyte lysates. We chose proteins that include amino and carboxyl extensions as well as proteins that are made up entirely of WD-repeats. We show that unlike G beta, several proteins with WD-repeats are able to fold into globular proteins in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate. One protein, beta Trcp, formed large aggregates like G beta, suggesting that it may also require a partner protein. Despite the presence of many potential tryptic cleavage sites, all of the proteins that did fold gave stable large products on tryptic proteolysis, as predicted on the basis of the structure of G beta. These studies suggest that other WD-repeat proteins are likely to form propeller structures similar to G beta.
- Sondek J, Bohm A, Lambright DG, Hamm HE, Sigler PB
- Crystal structure of a G-protein beta gamma dimer at 2.1A resolution.
- Nature. 1996; 379: 369-74
- Display abstract
Many signalling cascades use seven-helical transmembrane receptors coupled to heterotrimeric G proteins (G alpha beta gamma) to convert extracellular signals into intracellular responses. Upon nucleotide exchange catalysed by activated receptors, heterotrimers dissociate into GTP-bound G alpha subunits and G beta gamma dimers, either of which can modulate many downstream effectors. Here we use multiwavelength anomalous diffraction data to solve the crystal structure of the beta gamma dimer of the G protein transducin. The beta-subunit is primarily a seven-bladed beta-propeller that is partially encircled by an extended gamma-subunit. The beta-propeller, which contains seven structurally similar WD repeats, defines the stereochemistry of the WD repeat and the probable architecture of all WD-repeat-containing domains. The structure details interactions between G protein beta- and gamma-subunits and highlights regions implicated in effector modulation for the conserved family of G protein beta gamma dimers.
- Dynlacht BD, Weinzierl RO, Admon A, Tjian R
- The dTAFII80 subunit of Drosophila TFIID contains beta-transducin repeats.
- Nature. 1993; 363: 176-9
- Display abstract
A key component of the RNA polymerase II transcriptional apparatus, TFIID, is a multi-protein complex containing the TATA box-binding protein (TBP) and at least seven tightly associated factors (TAFs). Although the functions of most TFIID subunits are unknown, it is clear that TAFs are not necessary for basal activity but that one or more are required for regulated transcription, and so behave as coactivators. The presence of multiple subunits indicates that there is an intricate assembly process and that TAFs may be responsible for other activities. We have described the properties of the subunit dTAFII110, which can interact directly with the transcriptional activator Sp1 (ref. 5). In addition, the largest subunit, dTAFII250, binds directly to TBP and links other TAFs to the complex. Here we describe the cloning, expression and partial characterization of the Drosophila TAF of M(r) 80,000, dTAFII80. Sequence analysis reveals that dTAFII80 contains several copies of the WD40 (beta-transducin) repeat. Moreover, dTAFII80 shares extended sequence similarity with an Arabidopsis gene, COP1, which encodes a putative transcription factor that is though to regulate development. We have expressed recombinant dTAFII80 and begun to characterize its interaction with other members of the TFIID complex. Purified recombinant dTAFII80 is unable to bind TBP directly or to interact strongly with the C-terminal domain of dTAFII250 (delta N250). Instead, dTAFII80 is only able to recognize and interact with a higher-order complex containing TBP, delta N250, 110 and 60. These findings suggest the formation of TFIID may require an ordered assembly of the TAFs, some of which bind directly to TBP and others that are tethered to the complex as a result of specific TAF/TAF interactions.
- Fong HK et al.
- Repetitive segmental structure of the transducin beta subunit: homology with the CDC4 gene and identification of related mRNAs.
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986; 83: 2162-6
- Display abstract
Retinal transducin, a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein (referred to as a G protein) that activates a cGMP phosphodiesterase in photoreceptor cells, is comprised of three subunits. We have identified and analyzed cDNA clones of the bovine transducin beta subunit that may be highly conserved or identical to that in other G proteins. From the cDNA nucleotide sequence of the entire coding region, the primary structure of a 340-amino acid protein was deduced. The encoded beta subunit has a Mr of 37,375 and is comprised of repetitive homologous segments arranged in tandem. Furthermore, significant homology in primary structure and segmental sequence exists between the beta subunit and the yeast CDC4 gene product. The Mr 37,375 beta subunit polypeptide is encoded by a 2.9-kilobase (kb) mRNA. However, there exists in retina other beta-related mRNAs that are divergent from the 2.9-kb mRNA on the basis of oligonucleotide and primer-extended probe hybridizations. All mammalian tissues and clonal cell lines that have been examined contain at least two beta-related mRNAs, usually 1.8 and 2.9 kb in length. These results suggest that the mRNAs are the processed products of a small number of closely related genes or of a single highly complex beta gene.
- Disease (disease genes where sequence variants are found in this domain)
-
SwissProt sequences and OMIM curated human diseases associated with missense mutations within the WD40 domain.
Protein Disease Peroxisomal targeting signal 2 receptor (O00628) (SMART) OMIM:601757: Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata, type 1
OMIM:215100:Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase IB subunit alpha (P43034) (SMART) OMIM:601545: Lissencephaly-1 ; Subcortical laminar heterotopia
OMIM:247200: Miller-Dieker lissencephaly syndromeDNA damage-binding protein 2 (Q92466) (SMART) OMIM:600811: Xeroderma pigmentosum, group E, DDB-negative subtype
OMIM:278740: - Metabolism (metabolic pathways involving proteins which contain this domain)
-
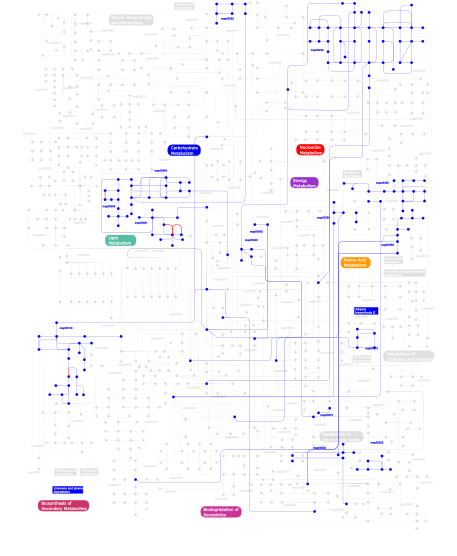
Click the image to view the interactive version of the map in iPath% proteins involved KEGG pathway ID Description 15.71 map04120 Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis 10.79 map04111 Cell cycle - yeast 9.05 map04310 Wnt signaling pathway 7.06 map04110 Cell cycle 6.13 map04530 Tight junction 4.93 map04810 Regulation of actin cytoskeleton 4.53 map04150 mTOR signaling pathway 3.99 map03022 Basal transcription factors 3.99 map04350 TGF-beta signaling pathway 3.99 map04730 Long-term depression 3.60 map04115 p53 signaling pathway 2.66 map04340 Hedgehog signaling pathway 2.53 map04140 Regulation of autophagy 2.40 map04080 Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction 2.13 map04914 Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation 2.00 map04910 Insulin signaling pathway 1.60  map00565
map00565Ether lipid metabolism 1.46 map04742 Taste transduction 1.46 map04210 Apoptosis 1.33 map05222 Small cell lung cancer 1.33  map00632
map00632Benzoate degradation via CoA ligation 0.93  map00562
map00562Inositol phosphate metabolism 0.40  map00350
map00350Tyrosine metabolism 0.40  map00340
map00340Histidine metabolism 0.40  map00642
map00642Ethylbenzene degradation 0.40  map00564
map00564Glycerophospholipid metabolism 0.40 map00960 Alkaloid biosynthesis II 0.40 map00903 Limonene and pinene degradation 0.40  map00310
map00310Lysine degradation 0.40  map00360
map00360Phenylalanine metabolism 0.40  map00624
map006241- and 2-Methylnaphthalene degradation 0.40  map00380
map00380Tryptophan metabolism 0.27  map00910
map00910Nitrogen metabolism 0.27 map05210 Colorectal cancer 0.13 map04370 VEGF signaling pathway 0.13 map04662 B cell receptor signaling pathway 0.13 map04020 Calcium signaling pathway 0.13 map04720 Long-term potentiation 0.13 map03060 Protein export 0.13 map04360 Axon guidance 0.13 map04010 MAPK signaling pathway 0.13  map00100
map00100Biosynthesis of steroids 0.13  map00561
map00561Glycerolipid metabolism 0.13 map02010 ABC transporters - General 0.13 map04660 T cell receptor signaling pathway 0.13  map00230
map00230Purine metabolism 0.13 map04330 Notch signaling pathway 0.13 map04650 Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity This information is based on mapping of SMART genomic protein database to KEGG orthologous groups. Percentage points are related to the number of proteins with WD40 domain which could be assigned to a KEGG orthologous group, and not all proteins containing WD40 domain. Please note that proteins can be included in multiple pathways, ie. the numbers above will not always add up to 100%.
- Structure (3D structures containing this domain)
3D Structures of WD40 domains in PDB
PDB code Main view Title 1a0r 
HETEROTRIMERIC COMPLEX OF PHOSDUCIN/TRANSDUCIN BETA-GAMMA 1b9x 
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF PHOSDUCIN AND ITS PHOSPHORYLATION-REGULATED INTERACTION WITH TRANSDUCIN 1b9y 
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF PHOSDUCIN AND ITS PHOSPHORYLATION-REGULATED INTERACTION WITH TRANSDUCIN BETA-GAMMA 1erj 
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE C-TERMINAL WD40 DOMAIN OF TUP1 1gg2 
G PROTEIN HETEROTRIMER MUTANT GI_ALPHA_1(G203A) BETA_1 GAMMA_2 WITH GDP BOUND 1got 
HETEROTRIMERIC COMPLEX OF A GT-ALPHA/GI-ALPHA CHIMERA AND THE GT-BETA-GAMMA SUBUNITS 1gp2 
G PROTEIN HETEROTRIMER GI_ALPHA_1 BETA_1 GAMMA_2 WITH GDP BOUND 1gxr 
WD40 Region of Human Groucho/TLE1 1k8k 
Crystal Structure of Arp2/3 Complex 1nex 
Crystal Structure of ScSkp1-ScCdc4-CPD peptide complex 1nr0 
Two Seven-Bladed Beta-Propeller Domains Revealed By The Structure Of A C. elegans Homologue Of Yeast Actin Interacting Protein 1 (AIP1). 1omw 
Crystal Structure of the complex between G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 and Heterotrimeric G Protein beta 1 and gamma 2 subunits 1p22 
Structure of a beta-TrCP1-Skp1-beta-catenin complex: destruction motif binding and lysine specificity on the SCFbeta-TrCP1 ubiquitin ligase 1pev 
Crystal Structure of the Actin Interacting Protein from Caenorhabditis Elegans 1pgu 
YEAST ACTIN INTERACTING PROTEIN 1 (AIP1), Se-Met PROTEIN, MONOCLINIC CRYSTAL FORM 1pi6 
YEAST ACTIN INTERACTING PROTEIN 1 (Aip1), ORTHORHOMBIC CRYSTAL FORM 1r5m 
Crystal Structure Of The C-Terminal WD40 Domain Of Sif2 1s4u 
Crystal Structure analysis of the beta-propeller protein Ski8p 1sq9 
Structure of Ski8p, a WD repeat protein involved in mRNA degradation and meiotic recombination 1tbg 
BETA-GAMMA DIMER OF THE HETEROTRIMERIC G-PROTEIN TRANSDUCIN 1trj 
Homology Model of Yeast RACK1 Protein fitted into 11.7A cryo-EM map of Yeast 80S Ribosome 1tyq 
Crystal structure of Arp2/3 complex with bound ATP and calcium 1u2v 
Crystal structure of Arp2/3 complex with bound ADP and calcium 1u4c 
Structure of spindle checkpoint protein Bub3 1vyh 
PAF-AH Holoenzyme: Lis1/Alfa2 1xhm 
The Crystal Structure of a Biologically Active Peptide (SIGK) Bound to a G Protein Beta:Gamma Heterodimer 1yfq 
High resolution S. cerevisiae Bub3 mitotic checkpoint protein 2aq5 
Crystal Structure of Murine Coronin-1 2b4e 
Crystal Structure of Murine Coronin-1: monoclinic form 2bcj 
Crystal Structure of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 in Complex with Galpha-q and Gbetagamma Subunits 2ce8 
An EH1 peptide bound to the Groucho-TLE WD40 domain. 2ce9 
A WRPW peptide bound to the Groucho-TLE WD40 domain. 2cnx 
WDR5 and Histone H3 Lysine 4 dimethyl complex at 2.1 angstrom 2co0 
WDR5 and unmodified Histone H3 complex at 2.25 angstrom 2g99 
Structural basis for the specific recognition of methylated histone H3 lysine 4 by the WD-40 protein WDR5 2g9a 
Structural basis for the specific recognition of methylated histone H3 lysine 4 by the WD-40 protein WDR5 2gnq 
Structure of wdr5 2h13 
Crystal structure of WDR5/histone H3 complex 2h14 
Crystal of WDR5 (apo-form) 2h68 
Histone H3 recognition and presentation by the WDR5 module of the MLL1 complex 2h6k 
Histone H3 recognition and presentation by the WDR5 module of the MLL1 complex 2h6n 
Histone H3 recognition and presentation by the WDR5 module of the MLL1 complex 2h6q 
Histone H3 recognition and presentation by the WDR5 module of the MLL1 complex 2h9l 
WDR5delta23 2h9m 
WDR5 in complex with unmodified H3K4 peptide 2h9n 
WDR5 in complex with monomethylated H3K4 peptide 2h9p 
WDR5 in complex with trimethylated H3K4 peptide 2hes 
Cytosolic Iron-sulphur Assembly Protein- 1 2i3s 
Bub3 complex with Bub1 GLEBS motif 2i3t 
Bub3 complex with Mad3 (BubR1) GLEBS motif 2o9k 
WDR5 in Complex with Dimethylated H3K4 Peptide 2oit 
Crystal Structure of the N-terminal Domain of the Human Proto-oncogene Nup214/CAN 2ovp 
Structure of the Skp1-Fbw7 complex 2ovq 
Structure of the Skp1-Fbw7-CyclinEdegC complex 2ovr 
Structure of the Skp1-Fbw7-CyclinEdegN complex 2p9i 
Crystal Structure of bovine Arp2/3 Complex co-crystallized with ADP and crosslinked with gluteraldehyde 2p9k 
Crystal structure of bovine Arp2/3 complex co-crystallized with ATP and crosslinked with glutaraldehyde 2p9l 
Crystal Structure of bovine Arp2/3 complex 2p9n 
Crystal Structure of bovine Arp2/3 complex co-crystallized with ADP 2p9p 
Crystal Structure of bovine Arp2/3 complex co-crystallized with ADP 2p9s 
Structure of bovine Arp2/3 complex co-crystallized with ATP/Mg2+ 2p9u 
Crystal structure of bovine Arp2/3 complex co-crystallized with AMP-PNP and calcium 2pbi 
The multifunctional nature of Gbeta5/RGS9 revealed from its crystal structure 2pm6 
Crystal Structure of yeast Sec13/31 edge element of the COPII vesicular coat, native version 2pm7 
Crystal structure of yeast Sec13/31 edge element of the COPII vesicular coat, selenomethionine version 2pm9 
Crystal structure of yeast Sec13/31 vertex element of the COPII vesicular coat 2qxv 
Structural basis of EZH2 recognition by EED 2trc 
PHOSDUCIN/TRANSDUCIN BETA-GAMMA COMPLEX 2vdu 
Structure of trm8, m7G methylation enzyme 2xl2 
WDR5 IN COMPLEX WITH AN RBBP5 PEPTIDE RECRUITED TO NOVEL SITE 2xl3 
WDR5 IN COMPLEX WITH AN RBBP5 PEPTIDE AND HISTONE H3 PEPTIDE 2xu7 
Structural basis for RbAp48 binding to FOG-1 2xyi 
Crystal Structure of Nurf55 in complex with a H4 peptide 2yb8 
Crystal structure of Nurf55 in complex with Su(z)12 2yba 
Crystal structure of Nurf55 in complex with histone H3 2ymu 
Structure of a highly repetitive propeller structure 2ynn 
yeast betaprime COP 1-304 with KTKTN motif 2yno 
yeast betaprime COP 1-304H6 2ynp 
yeast betaprime COP 1-604 with KTKTN motif 3acp 
Crystal Structure of Yeast Rpn14, a Chaperone of the 19S Regulatory Particle of the Proteasome 3ah8 
Structure of heterotrimeric G protein Galpha-q beta gamma in complex with an inhibitor YM-254890 3bg0 
Architecture of a Coat for the Nuclear Pore Membrane 3bg1 
Architecture of a Coat for the Nuclear Pore Membrane 3c99 
Structural Basis of Histone H4 Recognition by p55 3c9c 
Structural Basis of Histone H4 Recognition by p55 3cfs 
Structural basis of the interaction of RbAp46/RbAp48 with histone H4 3cfv 
Structural basis of the interaction of RbAp46/RbAp48 with histone H4 3cik 
Human GRK2 in Complex with Gbetagamma subunits 3dm0 
Maltose Binding Protein fusion with RACK1 from A. thaliana 3dw8 
Structure of a Protein Phosphatase 2A Holoenzyme with B55 subunit 3dwl 
Crystal Structure of Fission Yeast Arp2/3 Complex Lacking the Arp2 Subunit 3dxk 
Structure of Bos Taurus Arp2/3 Complex with Bound Inhibitor CK0944636 3dxm 
Structure of Bos taurus Arp2/3 Complex with Bound Inhibitor CK0993548 3eg6 
Structure of WDR5 bound to MLL1 peptide 3ei1 
Structure of hsDDB1-drDDB2 bound to a 14 bp 6-4 photoproduct containing DNA-duplex 3ei2 
Structure of hsDDB1-drDDB2 bound to a 16 bp abasic site containing DNA-duplex 3ei3 
Structure of the hsDDB1-drDDB2 complex 3ei4 
Structure of the hsDDB1-hsDDB2 complex 3emh 
Structural basis of WDR5-MLL interaction 3ewe 
Crystal Structure of the Nup85/Seh1 Complex 3f3f 
Crystal structure of the nucleoporin pair Nup85-Seh1, space group P21 3f3g 
Crystal structure of the nucleoporin pair Nup85-Seh1, space group P212121 3f3p 
Crystal structure of the nucleoporin pair Nup85-Seh1, space group P21212 3fhc 
Crystal structure of human Dbp5 in complex with Nup214 3fm0 
Crystal structure of WD40 protein Ciao1 3fmo 
Crystal structure of the nucleoporin Nup214 in complex with the DEAD-box helicase Ddx19 3fmp 
Crystal structure of the nucleoporin Nup214 in complex with the DEAD-box helicase Ddx19 3frx 
Crystal Structure of the Yeast Orthologue of RACK1, Asc1. 3gfc 
Crystal Structure of Histone-binding protein RBBP4 3gre 
Crystal structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Vps15 WD repeat domain 3i2n 
Crystal Structure of WD40 repeats protein WDR92 3iiw 
Crystal structure of Eed in complex with a trimethylated histone H3K27 peptide 3iiy 
Crystal structure of Eed in complex with a trimethylated histone H1K26 peptide 3ij0 
Crystal structure of Eed in complex with a trimethylated histone H3K9 peptide 3ij1 
Crystal structure of Eed in complex with a trimethylated histone H4K20 peptide 3ijc 
Crystal structure of Eed in complex with NDSB-195 3iko 
Crystal structure of the heterotrimeric Sec13-Nup145C-Nup84 nucleoporin complex 3j2t 
An improved model of the human apoptosome 3j6x 
3J6X 3j6y 
3J6Y 3j77 
3J77 3j78 
3J78 3j7p 
3J7P 3j7r 
3J7R 3j80 
3J80 3j81 
3J81 3jag 
3JAG 3jah 
3JAH 3jai 
3JAI 3jaj 
3JAJ 3jam 
3JAM 3jan 
3JAN 3jap 
3JAP 3jaq 
3JAQ 3jb9 
3JB9 3jbt 
3JBT 3jcm 
3JCM 3jcr 
3JCR 3jct 
3JCT 3jpx 
EED: A Novel Histone Trimethyllysine Binder Within The EED-EZH2 Polycomb Complex 3jro 
NUP84-NUP145C-SEC13 edge element of the NPC lattice 3jrp 
SEC13 with NUP145C (AA109-179) insertion blade 3jzg 
Structure of EED in complex with H3K27me3 3jzh 
EED-H3K79me3 3jzn 
Structure of EED in apo form 3k26 
Complex structure of EED and trimethylated H3K4 3k27 
Complex structure of EED and trimethylated H3K9 3krw 
Human GRK2 in complex with Gbetgamma subunits and balanol (soak) 3krx 
Human GRK2 in complex with Gbetgamma subunits and balanol (co-crystal) 3mkq 
Crystal structure of yeast alpha/betaprime-COP subcomplex of the COPI vesicular coat 3mks 
Crystal Structure of yeast Cdc4/Skp1 in complex with an allosteric inhibitor SCF-I2 3mmy 
Structural and functional analysis of the interaction between the nucleoporin Nup98 and the mRNA export factor Rae1 3mxx 
Crystal structure of WDR5 mutant (S62A) 3mzk 
Sec13/Sec16 complex, S.cerevisiae 3mzl 
Sec13/Sec31 edge element, loop deletion mutant 3n0d 
Crystal structure of WDR5 mutant (W330F) 3n0e 
Crystal structure of WDR5 mutant (W330Y) 3odt 
Crystal structure of WD40 beta propeller domain of Doa1 3ow8 
Crystal Structure of the WD repeat-containing protein 61 3p4f 
Structural and biochemical insights into MLL1 core complex assembly and regulation. 3psc 
Bovine GRK2 in complex with Gbetagamma subunits 3psl 
Fine-tuning the stimulation of MLL1 methyltransferase activity by a histone H3 based peptide mimetic 3pvu 
Bovine GRK2 in complex with Gbetagamma subunits and a selective kinase inhibitor (CMPD101) 3pvw 
Bovine GRK2 in complex with Gbetagamma subunits and a selective kinase inhibitor (CMPD103A) 3rfg 
Crystal structure of the yeast RACK1 dimer in space group P63 3rfh 
Crystal structure of the yeast RACK1 dimer in space group P21 3rse 
Structural and biochemical characterization of two binding sites for nucleation promoting factor WASp-VCA on Arp2/3 complex 3sfz 
Crystal structure of full-length murine Apaf-1 3shf 
Crystal structure of the R265S mutant of full-length murine Apaf-1 3smr 
Crystal structure of human WD repeat domain 5 with compound 3sn6 
Crystal structure of the beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex 3ukr 
Crystal structure of Bos taurus Arp2/3 complex with bound inhibitor CK-666 3uku 
Structure of Arp2/3 complex with bound inhibitor CK-869 3ule 
Structure of Bos taurus Arp2/3 complex with bound inhibitor CK-869 and ATP 3ur4 
Crystal structure of human WD repeat domain 5 with compound 3uvk 
Crystal structure of WDR5 in complex with the WDR5-interacting motif of MLL2 3uvl 
Crystal structure of WDR5 in complex with the WDR5-interacting motif of MLL3 3uvm 
Crystal structure of WDR5 in complex with the WDR5-interacting motif of MLL4 3uvn 
Crystal structure of WDR5 in complex with the WDR5-interacting motif of SET1A 3uvo 
Crystal structure of WDR5 in complex with the WDR5-interacting motif of SET1B 3uzs 
Structure of the C13.28 RNA Aptamer Bound to the G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2-Heterotrimeric G Protein Beta 1 and Gamma 2 Subunit Complex 3v5w 
Human G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 in Complex with Soluble Gbetagamma Subunits and Paroxetine 3v7d 
Crystal Structure of ScSkp1-ScCdc4-pSic1 peptide complex 3vl1 
Crystal structure of yeast Rpn14 3vu4 
Crystal structure of Kluyvelomyces marxianus Hsv2 3w15 
Structure of peroxisomal targeting signal 2 (PTS2) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase in complex with Pex7p and Pex21p 3zwl 
Structure of eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF3i complex with eIF3b C-terminus (655-700) 4a08 
Structure of hsDDB1-drDDB2 bound to a 13 bp CPD-duplex (purine at D-1 position) at 3.0 A resolution (CPD 1) 4a09 
Structure of hsDDB1-drDDB2 bound to a 15 bp CPD-duplex (purine at D-1 position) at 3.1 A resolution (CPD 2) 4a0a 
Structure of hsDDB1-drDDB2 bound to a 16 bp CPD-duplex (pyrimidine at D-1 position) at 3.6 A resolution (CPD 3) 4a0b 
Structure of hsDDB1-drDDB2 bound to a 16 bp CPD-duplex (pyrimidine at D-1 position) at 3.8 A resolution (CPD 4) 4a0k 
STRUCTURE OF DDB1-DDB2-CUL4A-RBX1 BOUND TO A 12 BP ABASIC SITE CONTAINING DNA-DUPLEX 4a0l 
Structure of DDB1-DDB2-CUL4B-RBX1 bound to a 12 bp abasic site containing DNA-duplex 4a11 
Structure of the hsDDB1-hsCSA complex 4a7j 
Symmetric Dimethylation of H3 Arginine 2 is a Novel Histone Mark that Supports Euchromatin Maintenance 4aez 
Crystal Structure of Mitotic Checkpoint Complex 4aow 
Crystal structure of the human Rack1 protein at a resolution of 2.45 angstrom 4av8 
Kluyveromyces lactis Hsv2 complete loop 6CD 4av9 
Kluyveromyces lactis Hsv2 4bh6 
Insights into degron recognition by APC coactivators from the structure of an Acm1-Cdh1 complex 4bl0 
Crystal structure of yeast Bub3-Bub1 bound to phospho-Spc105 4bts 
4BTS 4buj 
Crystal structure of the S. cerevisiae Ski2-3-8 complex 4bzj 
The structure of the COPII coat assembled on membranes 4bzk 
The structure of the COPII coat assembled on membranes 4ci8 
Crystal structure of the tandem atypical beta-propeller domain of EML1 4cy1 
Crystal structure of the KANSL1-WDR5 complex. 4cy2 
Crystal structure of the KANSL1-WDR5-KANSL2 complex. 4cy3 
Crystal structure of the NSL1-WDS complex. 4cy5 
Crystal structure of the NSL1-WDS-NSL2 complex. 4czv 
4CZV 4czx 
4CZX 4czy 
4CZY 4d0k 
4D0K 4d5l 
4D5L 4d61 
4D61 4d6v 
4D6V 4e54 
Damaged DNA induced UV-damaged DNA-binding protein (UV-DDB) dimerization and its roles in chromatinized DNA repair 4e5z 
Damaged DNA induced UV-damaged DNA-binding protein (UV-DDB) dimerization and its roles in chromatinized DNA repair 4erq 
X-ray structure of WDR5-MLL2 Win motif peptide binary complex 4ery 
X-ray structure of WDR5-MLL3 Win motif peptide binary complex 4erz 
X-ray structure of WDR5-MLL4 Win motif peptide binary complex 4es0 
X-ray structure of WDR5-SETd1b Win motif peptide binary complex 4esg 
X-ray structure of WDR5-MLL1 Win motif peptide binary complex 4ewr 
X-ray structure of WDR5-SETd1a Win motif peptide binary complex 4exv 
Structure of Kluyveromyces lactis Hsv2p 4fhl 
Nucleoporin Nup37 from Schizosaccharomyces pombe 4fhm 
Nup37-Nup120(aa1-961) complex from Schizosaccharomyces pombe 4fhn 
Nup37-Nup120 full-length complex from Schizosaccharomyces pombe 4g56 
Crystal Structure of full length PRMT5/MEP50 complexes from Xenopus laevis 4gga 
Structural Analysis of Human Cdc20 Supports Multi-site Degron Recognition by APC/C 4ggc 
Structural Analysis of Human Cdc20 Supports Multi-site Degron Recognition by APC/C 4ggd 
Structural analysis of human Cdc20 supports multisite degron recognition by APC/C. 4gm3 
Crystal structure of human WD repeat domain 5 with compound MM-101 4gm8 
Crystal structure of human WD repeat domain 5 with compound MM-102 4gm9 
Crystal structure of human WD repeat domain 5 with compound MM-401 4gmb 
Crystal structure of human WD repeat domain 5 with compound MM-402 4gq1 
Nup37 of S. pombe 4gq2 
S. pombe Nup120-Nup37 complex 4gqb 
Crystal Structure of the human PRMT5:MEP50 Complex 4h5i 
Crystal Structure of the Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor Sec12 (P1 form) 4h5j 
Crystal Structure of the Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor Sec12 (P64 form) 4i79 
Crystal structure of human NUP43 4ia9 
Crystal structure of human WD REPEAT DOMAIN 5 in complex with 2-chloro-4-fluoro-3-methyl-N-[2-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-5-nitrophenyl]benzamide 4j0w 
Structure of U3-55K 4j0x 
Structure of Rrp9 4j73 
Crystal structure of beta'-COP/p25 complex 4j77 
Crystal structure of beta'-COP/hWbp1 complex 4j78 
Crystal structure of beta'-COP/Emp47p complex 4j79 
Crystal structure of beta'-COP/PEDVspike complex 4j81 
Crystal structure of beta'-COP/Insig-1 complex 4j82 
Crystal structure of beta'-COP/Insig-2 complex 4j84 
Crystal structure of beta'-COP/Scyl1 complex 4j86 
Crystal structure of beta'-COP/yWbp1 complex 4j87 
Crystal structure of alpha-COP 4j8b 
Crystal structure of alpha-COP/Emp47p complex 4j8g 
Crystal structure of alpha-COP/E19 complex 4jd2 
Crystal structure of Bos taurus Arp2/3 complex binding with Mus musculus GMF 4jsn 
structure of mTORdeltaN-mLST8 complex 4jsp 
structure of mTORDeltaN-mLST8-ATPgammaS-Mg complex 4jsv 
mTOR kinase structure, mechanism and regulation. 4jsx 
structure of mTORDeltaN-mLST8-Torin2 complex 4jt5 
mTORdeltaN-mLST8-pp242 complex 4jt6 
structure of mTORDeltaN-mLST8-PI-103 complex 4jxm 
Crystal structure of RRP9 WD40 repeats 4kfm 
Crystal structure of the G protein-gated inward rectifier K+ channel GIRK2 (Kir3.2) in complex with the beta-gamma G protein subunits 4kzx 
Rabbit 40S ribosomal subunit in complex with eIF1. 4kzy 
Rabbit 40S ribosomal subunit in complex with eIF1 and eIF1A. 4kzz 
Rabbit 40S ribosomal subunit in complex with mRNA, initiator tRNA and eIF1A 4l9o 
Crystal Structure of the Sec13-Sec16 blade-inserted complex from Pichia pastoris 4lg8 
Crystal structure of PRPF19 WD40 repeats 4lg9 
Crystal structure of TBL1XR1 WD40 repeats 4mk0 
Crystal structure of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in complex with a a rationally designed paroxetine derivative 4n14 
4N14 4nsx 
Crystal Structure of the Utp21 tandem WD Domain 4o45 
WDR5 in complex with influenza NS1 C-terminal tail 4o9d 
Structure of Dos1 propeller 4owr 
4OWR 4ozu 
4OZU 4pby 
4PBY 4pbz 
4PBZ 4pc0 
4PC0 4pnk 
4PNK 4psw 
4PSW 4psx 
4PSX 4ql1 
4QL1 4qqe 
4QQE 4r7a 
4R7A 4u1e 
4U1E 4u3m 
4U3M 4u3n 
4U3N 4u3u 
4U3U 4u4n 
4U4N 4u4o 
4U4O 4u4q 
4U4Q 4u4r 
4U4R 4u4u 
4U4U 4u4y 
4U4Y 4u4z 
4U4Z 4u50 
4U50 4u51 
4U51 4u52 
4U52 4u53 
4U53 4u55 
4U55 4u56 
4U56 4u6f 
4U6F 4u7a 
4U7A 4uer 
4UER 4ug0 
4UG0 4ui9 
4UI9 4ujc 
4UJC 4ujd 
4UJD 4uje 
4UJE 4v16 
4V16 4v3p 
4V3P 4v5o 
4V5O 4v5z 
4V5Z 4v6i 
4V6I 4v6w 
4V6W 4v6x 
4V6X 4v7e 
4V7E 4v7f 
4V7F 4v7h 
4V7H 4v7r 
4V7R 4v88 
4V88 4v8m 
4V8M 4v8y 
4V8Y 4v8z 
4V8Z 4v92 
4V92 4wjs 
4WJS 4wju 
4WJU 4wjv 
4WJV 4x3e 
4X3E 4x60 
4X60 4x61 
4X61 4x63 
4X63 4xei 
4XEI 4xf2 
4XF2 4xfv 
4XFV 4xmm 
4XMM 4xmn 
4XMN 4xyh 
4XYH 4xyi 
4XYI 4y7r 
4Y7R 4ycz 
4YCZ 4yhc 
4YHC 4yvd 
4YVD 4zn4 
4ZN4 4zov 
4ZOV 4zox 
4ZOX 4zoy 
4ZOY 4zoz 
4ZOZ 5a1u 
5A1U 5a1v 
5A1V 5a1w 
5A1W 5a1x 
5A1X 5a1y 
5A1Y 5a2q 
5A2Q 5a31 
5A31 5a5u 
5A5U 5a9q 
5A9Q 5afu 
5AFU 5aj0 
5AJ0 5ams 
5AMS 5c9z 
5C9Z 5ch1 
5CH1 5ch2 
5CH2 5cvl 
5CVL 5cvn 
5CVN 5cvo 
5CVO 5cxb 
5CXB 5cxc 
5CXC 5cyk 
5CYK 5dat 
5DAT 5dc3 
5DC3 5dfz 
5DFZ 5eal 
5EAL 5eam 
5EAM 5eap 
5EAP 5ear 
5EAR 5em2 
5EM2 5emj 
5EMJ 5emk 
5EMK 5eml 
5EML 5emm 
5EMM 5fa5 
5FA5 5fci 
5FCI 5fcj 
5FCJ 5fl8 
5FL8 5flc 
5FLC 5flx 
5FLX 5fvm 
5FVM 5fxy 
5FXY 5g04 
5G04 5gan 
5GAN 5gap 
5GAP 5gm6 
5GM6 5gmk 
5GMK 5gxh 
5GXH 5gxi 
5GXI 5h1j 
5H1J 5h1k 
5H1K 5h1l 
5H1L 5h1m 
5H1M 5he0 
5HE0 5he1 
5HE1 5he2 
5HE2 5he3 
5HE3 5hqg 
5HQG 5hyn 
5HYN 5i4l 
5I4L 5ic7 
5IC7 5igo 
5IGO 5igq 
5IGQ 5ij7 
5IJ7 5ij8 
5IJ8 5it7 
5IT7 5it9 
5IT9 5jcs 
5JCS 5jpq 
5JPQ 5juo 
5JUO 5jup 
5JUP 5jus 
5JUS 5jut 
5JUT 5juu 
5JUU 5juy 
5JUY 5k0y 
5K0Y 5k19 
5K19 5k1a 
5K1A 5k1b 
5K1B 5k1c 
5K1C 5kc2 
5KC2 5kdo 
5KDO 5khr 
5KHR 5khu 
5KHU 5l8e 
5L8E 5l8w 
5L8W 5l9t 
5L9T 5l9u 
5L9U 5lcw 
5LCW 5lj3 
5LJ3 5lj5 
5LJ5 5lqw 
5LQW 5lyb 
5LYB 5lzs 
5LZS 5lzt 
5LZT 5lzu 
5LZU 5lzv 
5LZV 5lzw 
5LZW 5lzx 
5LZX 5lzy 
5LZY 5lzz 
5LZZ 5sxm 
5SXM 5tdh 
5TDH 5tee 
5TEE 5tef 
5TEF 5tf2 
5TF2 5tga 
5TGA 5tha 
5THA - Links (links to other resources describing this domain)
-
PROSITE WD_REPEATS PFAM WD40 INTERPRO IPR001680

